2.3-HTML
HTML
An HTML File:
HTML 指的是超文本标记语言: HyperText Markup Language
HTML 不是一种编程语言,而是一种标记语言
标记语言是一套标记标签 (markup tag)
.htm or .html file extension
Can be created using any text editor
HTML tags & HTML elements
html tage:
• Mark-up HTML elements.
• Surrounded by < >
• Normally come in pairs:
– start tag and end tag 开始标签和结束标签
– E.g. <title> and </title>
• The text between the start and end tags is the element content. 元素=标签+内容
• HTML tags are not case-sensitive. HTML 文档中的标签名和属性名都是大小写不敏感的
• HTML elements are defined using HTML tags e.g.
<title>My page</title>
• HTML documents are text files made up of HTML elements.
html中会忽略空格
基础结构

common tags
• Paragraphs <p> </p>
html段落前后会自动空行
<html>
<body>
<p>This is the 1st paragraph.</p>
<p>This is the 2nd paragraph.</p>
<p>This is the 3rd paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>• Headings <h> </h>
<html>
<body>
<h1>This is heading 1</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6</h6>
</body>
</html>• Line Breaks换行 <br />

<html>
<body>
<p>This paragraph has <br />
a line break here</p>
</body>
</html><br>//分割两段但不空行
单独用空一行
//没有结束标签,自己就是结束的证明Use <br> tag to enter line breaks, not to separate paragraphs. Browsers automatically add an empty line before and after a paragraph
Horizontal rule **
<hr>**水平分割线
<html>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
<hr>
<p>This is another paragraph</p>
<hr>
</body>
</html>- Comments in HTML
<html>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
<!-- This is a comment -->
<p>This is another paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>
HTML Attributes & HTML Text Formatting
HTML Attributes
Attributes provide additional information to an HTML element
A bit like Java method parameters
- Inside the start tag, name=“value”
以名称=“值”的形式出现,在开始标签里规定

Attributes and attribute values are case-insensitive, but the W3C recommends using lowercase.
HTML Text Formatting
• <b> Defines bold text.
• <big> Defines big text. (不在html5里,不用)
• <em> Defines emphasized text.
• <i> Defines italic text.
• <small> Defines small text.
• <strong> Defines strong text.
• <sub> Defines subscripted text. 下标
• <sup> Defines superscripted text. 上标
• <ins> Defines inserted text.
• <del> Defines deleted text.
<b>This text is bold</b><br/>
<strong>This text is strong</strong>
<big>This text is big</big>
<em>This text is emphasized</em>
<i>This text is italic</i>
<small>This text is small</small>
Character Entities
在 HTML 中,某些字符是预留的。在 HTML 中不能使用小于号(<)和大于号(>),这是因为浏览器会误认为它们是标签。在 HTML 源代码中使用字符实体(character entities)。注意分号


HTML Head
• The title of a document:
<head>
<title>The is the title</title>
</head>• For all:
<head>
<base target=“_blank”>
</head><base> 标签为页面上的所有链接规定默认地址或默认目标。
为所有该页面链接设置打开在新窗口
HTML Links
链接
tage:
文本链接:
HTML uses a hyperlink to link to another document on the Web:
<a href="url">Text to be displayed</a><a href=“linkpage.html”>This text</a> is a link to a page on
this Web site.
<a href=“http://www.qmul.ac.uk/”>This text</a> is a link to
QMUL
图片链接:
<p> Use an image as a link:
<a href=“linkpage.htm”><img border=“0”
src=“image.jpg” width=“65” height=“38”></a>
</p>href
Open link in a new browser window:
<a href=“http://www.qmul.ac.uk/”
target=“_blank”>Visit QMUL</a>Target: where to open the linked document

_blank
浏览器总在一个新打开、未命名的窗口中载入目标文档。
_self
这个目标的值对所有没有指定目标的 标签是默认目标,它使得目标文档载入并显示在相同的框架或者窗口中作为源文档。这个目标是多余且不必要的,除非和文档标题
_parent
这个目标使得文档载入父窗口或者包含来超链接引用的框架的框架集。如果这个引用是在窗口或者在顶级框架中,那么它与目标 _self 等效。
_top
这个目标使得文档载入包含这个超链接的窗口,用 _top 目标将会清除所有被包含的框架并将文档载入整个浏览器窗口。
提示:这些 target 的所有 4 个值都以下划线开始。任何其他用一个下划线作为开头的窗口或者目标都会被浏览器忽略,因此,不要将下划线作为文档中定义的任何框架 name 或 id 的第一个字符。
页面内跳转
<a name=“top”>This is the top of this page</a>
...
...
...
<a href=“section.html”#top>Jump to top of this page</a><p>
<a href="#C4">查看 Chapter 4。</a>
</p>
<h2><a name="C4">Chapter 4</a></h2>
<p>This chapter explains ba bla bla</p>HTML Tables
Table Tags
•**<table>** Defines a table.
• <th> Defines a table header.
• <tr> Defines a table row. 定义 HTML 表格中的行
• <td> Defines a table cell.
HTML 表单中有两种类型的单元格:
- 表头单元格 - 包含表头信息(由 th 元素创建)
- 标准单元格 - 包含数据(由 td 元素创建)
th 元素内部的文本通常会呈现为居中的粗体文本,而 td 元素内的文本通常是左对齐的普通文本。
• <caption> Defines a table caption.
• <thead> Defines a table head.
• <tbody> Defines a table body.
• <tfoot> Defines a table footer.
<table border=“1”>
<caption> title </caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>h1</th>
<th>h2</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td>f1</td>
<td>f2</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>row 1, cell 1</td>
<td>row 1, cell 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>row 2, cell 1</td>
<td>row 2, cell 2</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>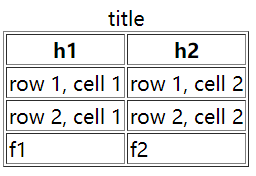
<table>标签定义 HTML 表格。简单的 HTML 表格由 table 元素以及一个或多个 tr、th 或 td 元素组成。tr 元素定义表格行,th 元素定义表头,td 元素定义表格单元
border-规定边框宽度
• Add background colour:
<table border=“1” bgcolor=“red”>• Add background image:
<table border=“1” background=“bg.jpg”>• Align(对齐) the text:
<tr>
<td align=“left”>To left</td>
<td align=“right”>To right</td>
<td align=“center”>To center</td>
</tr>HTML Lists
Unordered list:
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
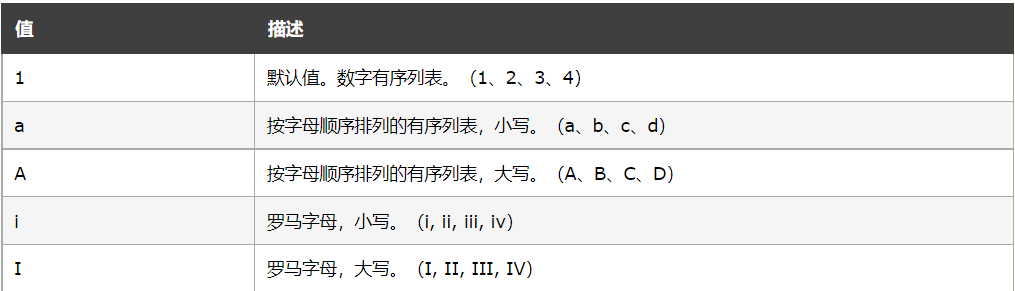
Ordered list:
<ol>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol><ol type=“A”>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>
<ol type=“a”>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>
<ol type=“I”>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>
<ol type=“i”>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>效果图:

HTML Images & Colour
• Insert an image :
<img src=“image.gif” width=“144” height=“50”>• The alt attribute is used to define an “alternate text” for an image:
<img src=“me.jpg” alt=“This is me”>
• Background image:
<body background=“background.jpg”>• Background colour:
<body bgcolor=“#d0d0d0”>• Text colour:
<body bgcolor=“#000000” text=“yellow”>
<embed>
• The
<embed> 标签定义嵌入的内容,比如插件。
<embed src="helloworld.swf">**HTML Forms **
• HTML Forms are used to select different kinds of user input.
HTML 表单用于搜集不同类型的用户输入。
基本格式
<form>
<input>
<input>
</form>创建表单,表单用于给服务器传递数据
Attribute
action:
The form’s action attribute defines the name of the file to send the content to.用于处理表单的服务器端页面(以URL 形式表示)
method
不指定method,默认为get
点击submit且form为get方法,会向action的页面提交 每一个控件的“name-value对”(长度有限制)
点击submit且form为post方法,则数据在http的entity body中(可以打开浏览器中的源代码查看)
并且会提交所有拥有name的input的键值对(以&隔开)
格式为http://www.example.com?name=value
表单项要想被提交则必须指定 input中的name属性
tag列表

表单项
包括:
<input>
<select>
<label>
<textarea>
<Fieldset>
input
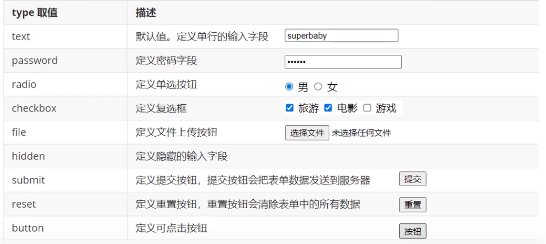
• The most used form tag is the tag. The type of input is specified with the type attribute. 标签用于搜集用户信息。根据不同的 type 属性值,输入字段拥有很多种形式。输入字段可以是文本字段、复选框、掩码后的文本控件、单选按钮、按钮等等。
标签没有结束标签。
input中的属性
type:
name属性:The name attribute is what is sent when the form is submitted.
The name is the identifier that is sent to the server when you submit the form.
ID属性:The id attribute uniquely identifies any element on the page
difference between name and id
id可以唯一标识,name可以标识多个值
- value属性:

Text fields

<form action=“”>
First name:
<input type=“text” name=“firstname”>
<br>
Last name:
<input type=“text” name=“lastname”>
</form>form表单中input的text类型字段如果不填值的话,默认值为空串,即“”(不是null)
Password Fields

<form action=“”>
Username:
<input type=“text” name=“user”>
<br>
Password:
<input type=“password” name=“password”>
</form>When you type characters in a password field, the browser displays asterisks or bullet points instead of the characters.
Radio buttons
单选框Select one of the choices.
<form>
<input type="radio"
name="sex"
value="male"> Male
<br>
<input type="radio"
name="sex"
value="female"> Female
</form>如果两个选项name一样,两个选择项互斥
Checkboxes
复选框Select one or more options.

<form>
I have a bike:
<input type=“checkbox”
name=“vehicle”
value=“Bike”>
<br>
I have a car:
<input type=“checkbox”
name="vehicle"
value=“Car”>
<br>
I have an airplane:
<input type=“checkbox”
name=“vehicle”
value=“Airplane”>
</form>Defining <label> for button
• The
This allows a user to click on the label as well as the button
• The for attribute of the should be equal to the id attribute of the related element“for” 属性可把 label 绑定到另外一个元素。请把 “for” 属性的值设置为相关元素的 id 属性的值。
<form action="demo_form.asp">
<label for="male"> Male </label>
<input type="radio" name="sex" id="male"
value="male"><br>
<label for="female">Female</label>
<input type="radio" name="sex" id="female"
value="female"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>Submit Button
When the user clicks on the “Submit” button, the content of the form is sent to another file.
发邮件的例子:
mailto: 邮箱地址
<form action=“MAILTO:yourname@company.com”
method=“post” enctype=“text/plain”>
Name:<br>
<input type=“text” name=“name” size=“20”>
<br>
Mail:<br>
<input type=“text” name=“mail” size=“20”>
<br>
Comment:<br>
<input type=“text” name=“comment” size=“40”>
<br><br>
<input type=“submit” value=“Send”>
<input type=“reset” value=“Reset”>
</form>The file defined in the action attribute usually does something with the received input.
<form name=“input” action=“html_form_action.jsp”
method=“get”>
Username:
<input type=“text” name=“user”>
<input type=“submit” value=“Submit”>
</form>Image acts as a submit button
<input type="image" src="path to image" name="submit" />The image type is by default a form submitting button.

Button
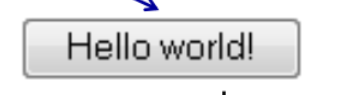
<form action=“”>
<input type=“button” value=“Hello world!”>
</form>Difference between button and submit
• buttons will not submit a form on their own - they don’t do anything by default.
• buttons will submit the form they are in when the user clicks on them, unless you specify otherwise with JavaScript
– But depends on browser! having a form, without a submit-button but instead a









