2.2-HTTP
HTTP
http
HyperText Transfer Protocol
An application layer protocol used to transfer web pages (and other content) from a sever to a client
What is a web page?
A web page consists of objects:
– e.g. an HTML file, a JPEG image, an audio clip, an applet that are addressable by a single URL;
– also called a document.
Usually consists of a base HTML document and several other referenced objects.

CLIENT-SERVER WEB ARCHITECTURE

- A Server
exposes a listening socket Send a response containing e.g. html (other referenced resources)
Extract (and validate) user data, perform task and send response.
- A Client
software that initiates a request
Send a request for the resource/document (webpage) addressable by ONE URL :
HTTP follow the client-server model
Context of HTTP
HTTP is an application-layer protocol( it operates at the top of the OSI)
It relies on many other protocols to achieve its goals:
– TCP provides reliable in-order delivery
– IP delivers data packets between the end hosts (i.e. client and server)
– Layer 2 (e.g. Ethernet) protocols deal with the individual networks (MAC)
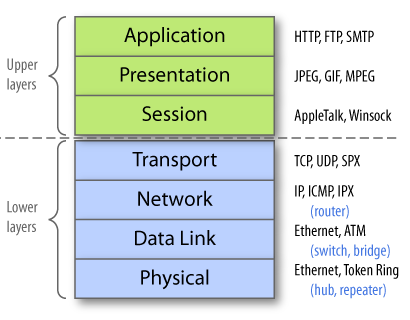
Network Layer delivers data packets between end hosts
Transport Layer delivers data segments between processes
Application Layer delivers services and applications Deals with advanced application specific functionality,
Each layer adds routing information
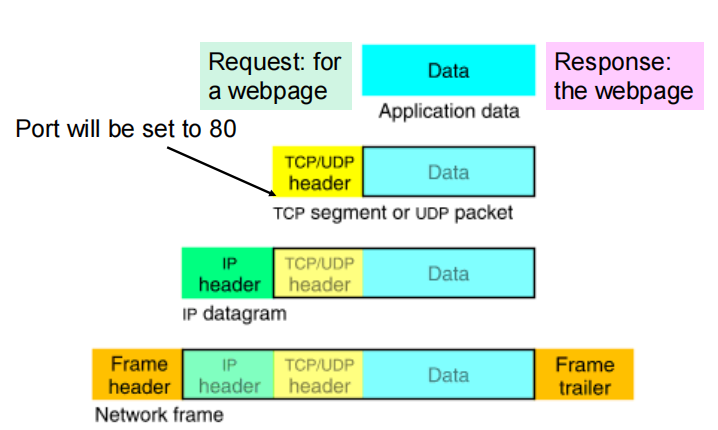
HTTP and TCP
HTTP is built over TCP
Socket socket = new Socket(“10.0.0.1”, 80)就是建立TCP连接的过程
– Initiates a TCP connection to 10.0.0.1’s port 80
TCP makes life much easier for HTTP
– No (perceived) packet loss
– No out-of-order delivery
– Congestion/flow control automatically handled
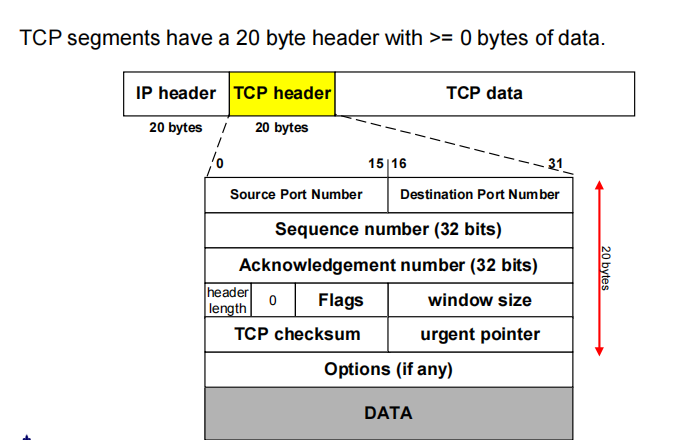
TCP
TCP = Transmission Control Protocol
Connection-oriented protocol
Provides a reliable unicast(单播) 可靠的点对点传播 (i.e., one-to-one) end-to-end byte stream over an unreliable internetwork
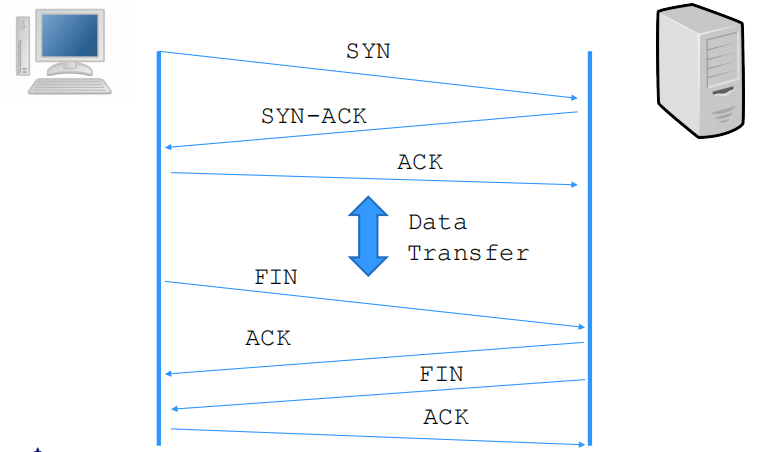
Before any data transfer, TCP establishes a connection(建立socket时):
– One TCP entity is waiting for a connection (“server”)
– The other TCP entity (“client”) contacts the server
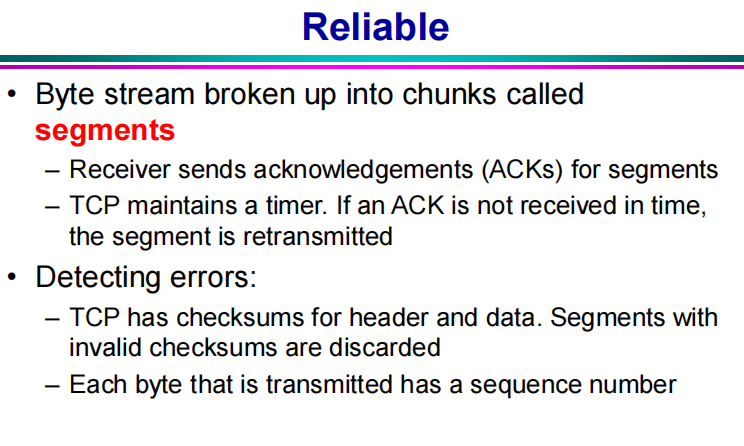
To the higher layers, TCP exposes a byte stream service
– i.e., OutputStream in your Socket class
在更高层看来TCP提供流服务,看不到报文段
• System services reserve the use of ports 0 through 1023.
– Do not use them!
• Default port for web server is port 80
URL: Uniform Resource Locator
HTTP使用统一资源标识符(Uniform Resource Identifiers, URI)来传输数据和建立连接。
A way of locating a resource on the Internet
– a file, an e-mail address, a CGI program
protocol://hostname[:port]/path/filename#sectionprotocol– the protocol used to access the server
hostname– the name of the server
/path/filename– the location of a file on the server
Points to a file in the directory specified by path:
if omitted, it is left to the server to decide which file to send
• e.g. it may send an index of the directory, often in a file called index.html
path - 定义服务器上的路径(如果省略,则文档必须位于网站的根目录中)。
#section is a named anchor in an HTML document:
– also called fragment or Ref
– created using a tag 与HTML中的标签相连
<A NAME="abc123"> </A>in the HTML file specified
fragment可以理解为资源内部的书签.用来想服务器指明展示的内容所在的书签的点.例如对于HTML文件来说,浏览器会滚动到特定的或者上次浏览过的位置.对于音频或者视频资源来说,浏览器又会跳转到对应的时间节点.
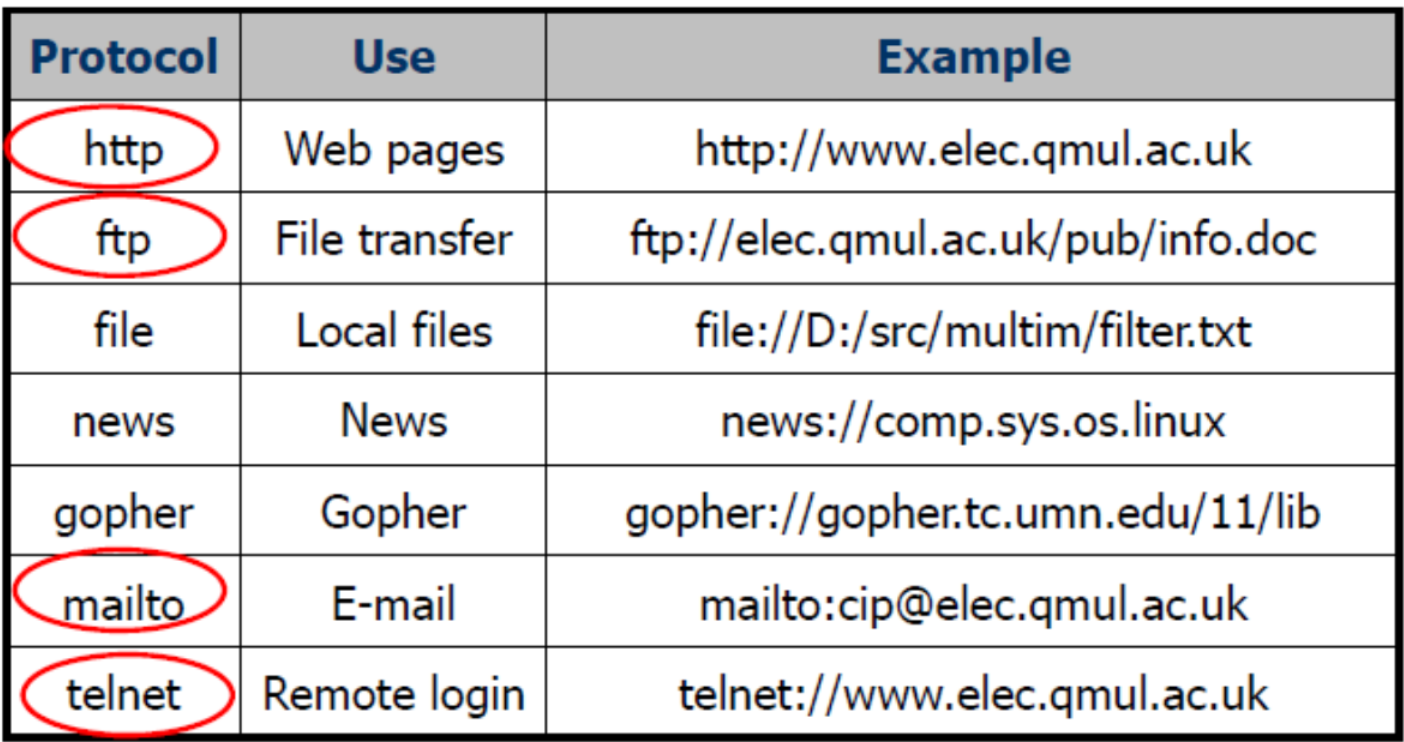
Other possible protocols to use with URLs
HTTP PROTOCOL DETAILS
无状态:It is stateless: it does not remember anything about previous connections, so it’s simple and robust
can lead to inefficiencies:client请求一个页面,然而这个页面没变化,就需要重发

HTTP/1.0, HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2.0 use TCP as the underlying transport protocol.
– Client writes HTTP request messages into its socket and reads responses from the socket.
– Server reads HTTP requests and writes it responses to its sockets**.**
持续连接与非持续
persistent connection:一个请求建立一个TCP
Server leaves a TCP connection open (for some time) after sending a response.Subsequent requests and responses between same client and server can be made over same connection
Usually multiple resources are obtained by parallel TCP connections
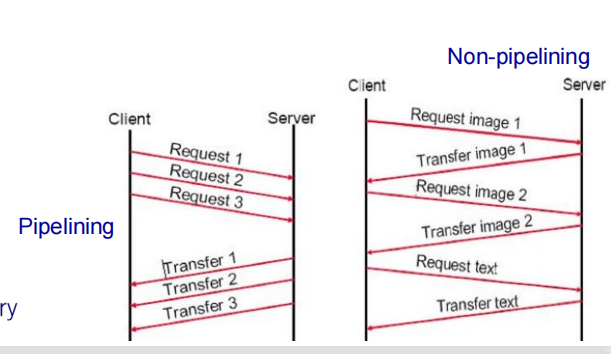
non-persistent connection:一系列请求基于一个相同的TCP
非流水线方式: 客户在收到前一个响应后才能发出下 一个请求。这比非持续连接的两倍 RTT 的开销节省了 建立 TCP 连接所需的一个 RTT时间。但服务器在发 送完一个对象后,其 TCP 连接就处于空闲状态,浪费 了服务器资源。
流水线方式: 客户在收到 HTTP的响应报文之前就能够接着发送新的请求报文。一个接一个的请求报文到 达服务器后,服务器就可连续发回响应报文。使用流水线方式时,客户访问所有的对象只需花费一个 RTT 时间,使 TCP 连接中的空闲时间减少,提高了下载文档效率。
http 1.1及以后才支持persistent connection 和pipeline
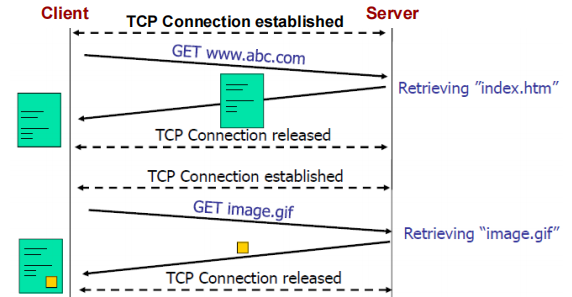
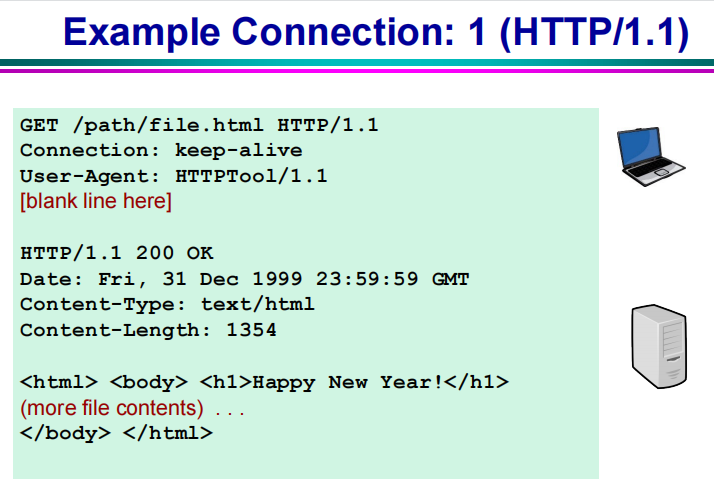
建立HTTP过程(no-persistent connection):
1个HTTP响应对应一个TCP连接
Set up TCP connection from client to server.
HTTP client sends a message to the server requesting the page at specified URL using the TCP connection established in step 1.– Request includes the path name.
HTTP server receives message via connection socket set up in step 1 and then:
– retrieves the requested object from its data storage;
– encapsulates the object in an HTTP response message;
– sends the response back via the connection socket.
HTTP server tells TCP to close connection.
– TCP doesn’t actually do this until the client has successfully received the response.
Client receives message, and the TCP connection terminates.
The message tells the client that the response object is an HTML file.
– Client extracts the file from the response message, parses the HTML file and finds references to other referenced objects.
7. Steps 1-5 are repeated for each of these referenced objects.

如果是persistent connections 所有element in HTML都经过这一个TCP传
HTTP message format
HTTP报文结构和内容(转) - myseries - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
HTTP有两种报文:请求报文和响应报文
请求报文
Two key HTTP request methods:
– GET
• Query string incorporated in the request URL.
• Idempotent(幂等性): multiple requests have the same effect as a single one.
一次和多次请求某一个资源对于资源本身应该具有同样的结果(关注产生的影响而不是结果),也就是说任意执行对资源本身所产生的影响均与第一次执行的影响相同。
注意:(一次和多次结果中)可能返回得到不同的结果,当时并不影响资源
• Cachable.
– POST
• Query string placed in the body of the HTTP request. 不显示在URL
• Non-idempotent: e.g. pressing a shopping button twice would result in two orders!
• Used when e.g. want to alter data on the server-side
GET 用于获取信息,是无副作用的,是幂等的,且可缓存
POST 用于修改服务器上的数据,有副作用,非幂等,不可缓存
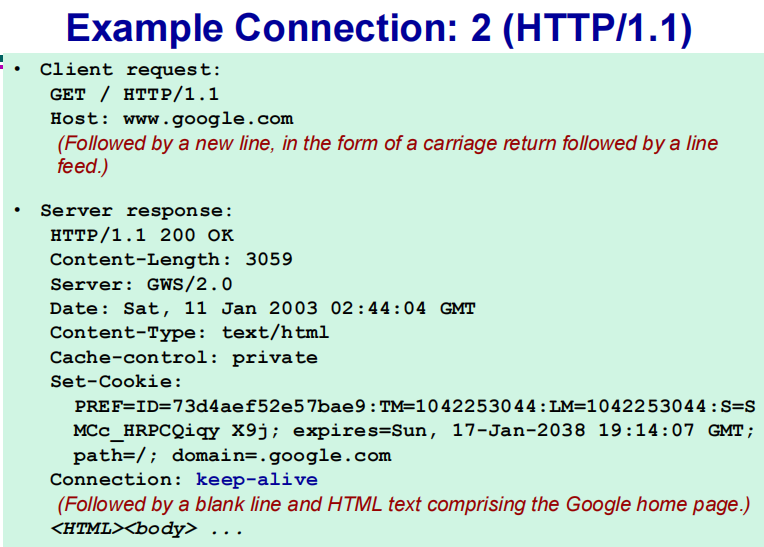
GET message request
GET /somedir/index.html HTTP/1.1
Host: www.qmul.ac.uk
Connection: close
User-agent: Mozilla/5.0
Accept-language:fr- ==第一行叫 request line==
请求行由三部分组成:请求方法,请求URL(不包括域名),HTTP协议版本请求方法比较多:GET、POST、HEAD、PUT、DELETE、OPTIONS、TRACE、CONNECT
最常用的是GET和POST。
==2-4行都是header line==
请求头部由关键字/值对组成,每行一对
User-Agent : 产生请求的浏览器类型
Connection:设置persistent connect 是否启用
Accept : 客户端希望接受的数据类型,比如 Accept:text/xml(application/json)表示希望接受到的是xml(json)类型
Content-Type:发送端发送的实体数据的数据类型。
比如,Content-Type:text/html(application/json)表示发送的是html类型。Host : 请求的主机名
请求头之后是一个空行(extra carriage return(回车) and line feed(换行)),通知服务器以下不再有请求头
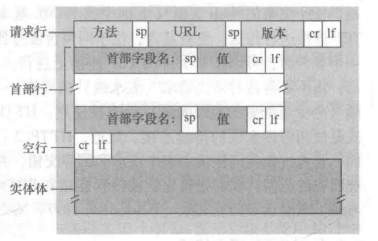
通用格式:
<request-line> //请求行
<headers> //首部行
<blank line> //空行
<entity body> //请求体(只有post有)This text is simply written into a socket!
request message format
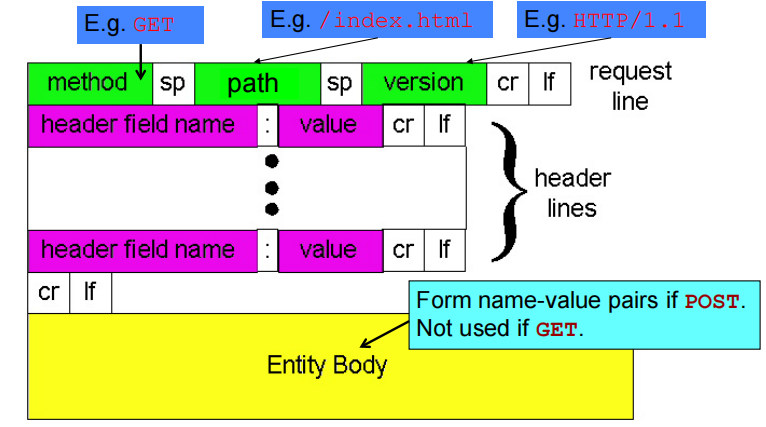
使用post时才使用entity body(用户的输入值)
A response message
HTTP响应报文和请求报文的结构差不多,也是由四个部分组成:
<status-line> //状态行
<headers> //消息报头
<blank line> //空行
<entity-body> //响应体HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Connection : close
Date: Fri, 10th Nov 2000 12:01:14 GMT
Server: Apache/1.3.0 (Unix)
Last-Modified: Mon, 20 July 1999 08:44:01 GMT
Content-Length: 5993
Content-Type: text/html
(data data data ...)初始状态行(status line)(服务器HTTP协议版本,响应状态码,状态码的文本描述)
常用状态码:
- 1xx:指示信息,表示请求已接收,继续处理
- 2xx:成功,表示请求已被成功接受,处理
- 3xx: 重定向,需要进一步的操作以完成请求
- 4xx:客户端错误
- 5xx:服务器端错误,服务器未能实现合法的请求

300:有多个返回对象
response message format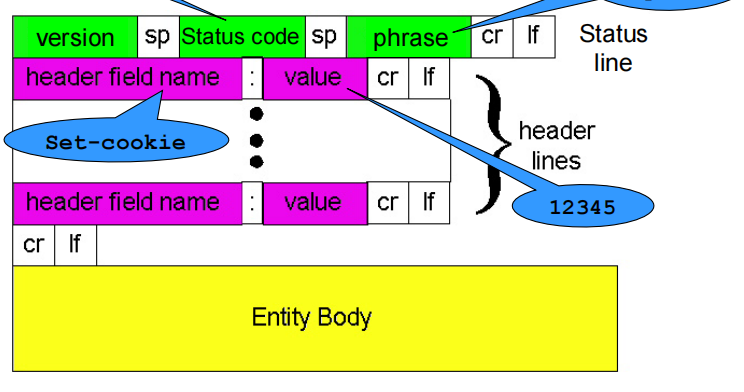

IMPORTANT HEADERS
Cache-Control 缓存控制
Holds instructions for caching in both requests and responses
服务器使用此Header来向客户端建议缓存策略(是否缓存该响应)
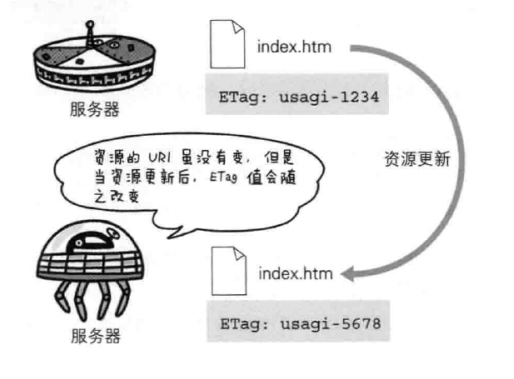
Etag
an identifier for a specific version of a resource
ETag是一个可以与Web资源关联的记号
Vary
Allows to determine if a cached response may be returned for a subsequent request
应该使用一个缓存作为响应还是向源服务器请求一个新的响应
Date
– Shows the timestamp of when the response was generated
显示生成响应的时间戳
Expires
– Shows the time that the resource expires
显示资源过期的时间
Pragma
Similar to cache-control (e.g. often used to disable caching)
Content-Length
– Shows the length of the resource in bytes
Content-Encoding
– Describes how the content is encoded, e.g. gzip
Content-Type
– MIME type of object, e.g. text/html
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) 是描述消息内容类型的标准,用来表示文档、文件或字节流的性质和格式。
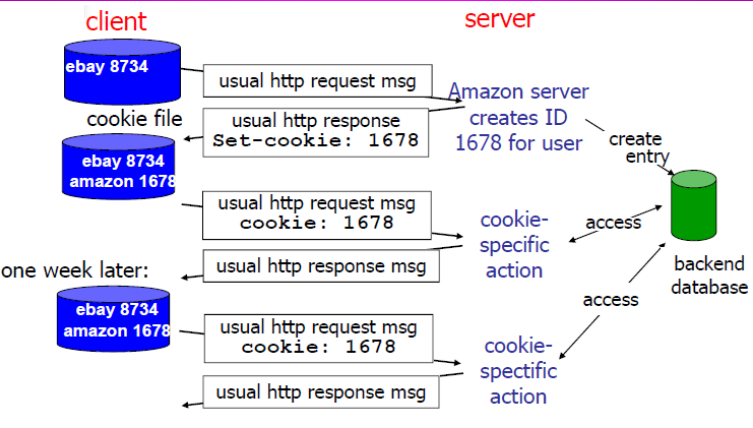
Set-Cookie Header
认识HTTP—-Cookie和Session篇 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
Many major websites use cookies.
Cookie 技术通过在请求和响应报文中写入Cookie 信息来控制客户端的状态。
Cookie 会根据从服务器端发送的响应报文内的一个叫做Set-Cookie的首部字段信息,通知客户端保存Cookie。当下次客户端再往该服务器发送请求时,客户端会自动在请求报文中加入Cookie 值后发送出去。服务器端发现客户端发送过来的Cookie 后,会去检查究竟是从哪一个客户端发来的连接请求,然后对比服务器上的记录,最后得到之前的状态信息。
cookie header line of HTTP response message;
cookie header line in HTTP request message;
cookie file kept on user’s host, managed by user’s browser;
backend database at website



When initial HTTP request arrives at site, site creates:
unique ID;
entry in backend database for ID
HTTPS
HTTP Secure
The same as HTTP but
– Runs over **TLS (Transport Layer Security)**不是基于TCP,基于TLS
– Port 443
All traffic (headers and payloads) are encrypted
HTTPS Issues
• Adds extra overhead
• Increases connection setup time
– Requires TCP setup + TLS handshake
Thus, increases page load time
The security of HTTPS depends on that of the underlying TLS protocol
Moreover, a website that uses mixed protocols (e.g., images served via HTTP, login info via HTTPS) can still make the user vulnerable to attacks/surveillance
HTTP 2.0
Initiated by the IETF to design a new version of HTTP
HTTP 2.0 has had a focus on reducing page load times
- Multiplexing
– Multiple resources can be requested and fetched in parallel
可以并行地请求和获取多个资源
– Prevents “head of line” blocking
- Universal encryption
– All traffic is encrypted by default
– Equivalent of running everything over HTTPS
- Server push/hint
– Server can push resources before being requested
服务器可以在请求之前推送资源
– Server can “hint” that clients fetch resources (e.g. if the server knows the client will need something in the future)
服务器可以“提示”客户端获取资源(例如,如果服务器知道客户端将来会需要某些东西)
- Content prioritization
– Specify the preferred order and priority that server transfers resources to clie
指定服务器向客户端传输资源的首选顺序和优先级









