互联网协议-Chapter 3 Network Layer
Network Layer
Overview
network-layer functions
▪forwarding: move packets from router’s input to appropriate router output(数据平面)路由器内
▪routing: determine route taken by packets from source to destination(控制平面)整个过程
Network layer
transport datagram from sending to receiving host
on sending side encapsulates segments into datagrams(把TCP报文段封装为IP数据报)
on receiving side, delivers segments to transport layer(把报文段上交给传输层)
network layer 存在于主机和路由器之中,但是路由器只有下三层,不具备transport和application的功能
router examines header fields in all IP datagrams passing through it(路由器检查datagram的header)
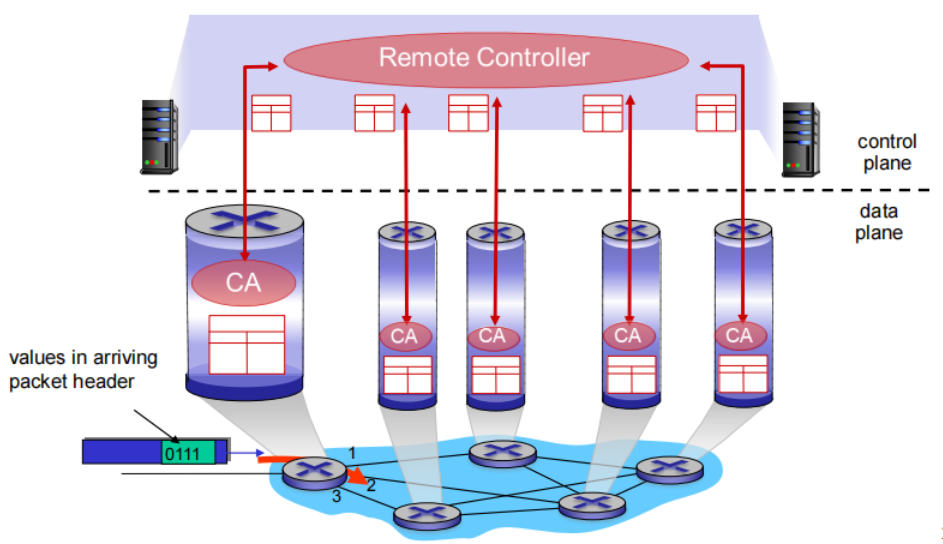
data plane, control plane
Data plane
local, per-router function
determines how datagram arriving on router input port is forwarded to router output port
forwarding function
Control plane
network-wide logic
determines how datagram is routed among routers along end-end path from source host to destination host
two control-plane approaches:
• traditional routing algorithms: implemented in routers(每个路由器实现转发和路由)
• software-defined networking (SDN): implemented in (remote) servers
traditional routing algorithms: Per-router control plane
Individual routing algorithm components in each and every router interact in the control plane
路由选择算法在每台路由器中运行,并且在每台路由器中都包含转发和路由两种功能
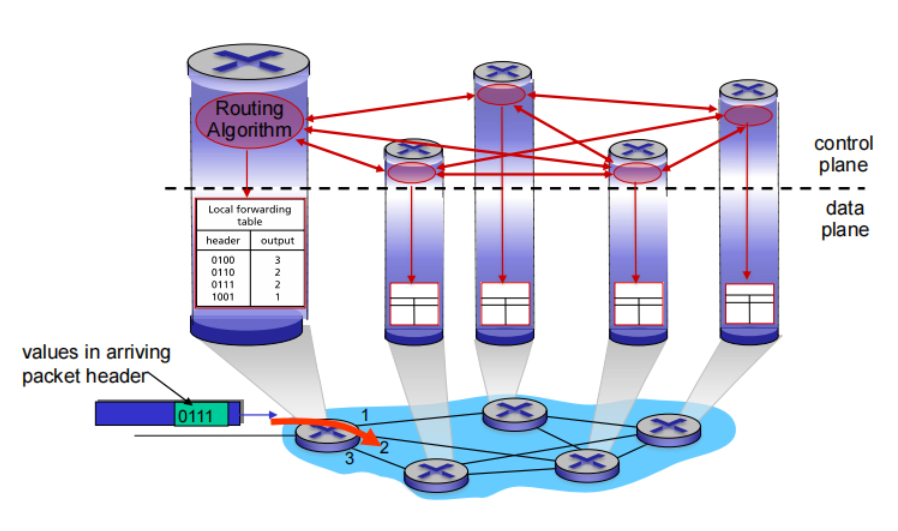
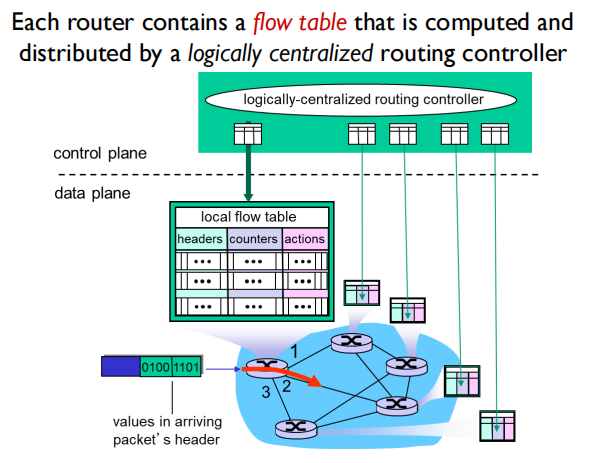
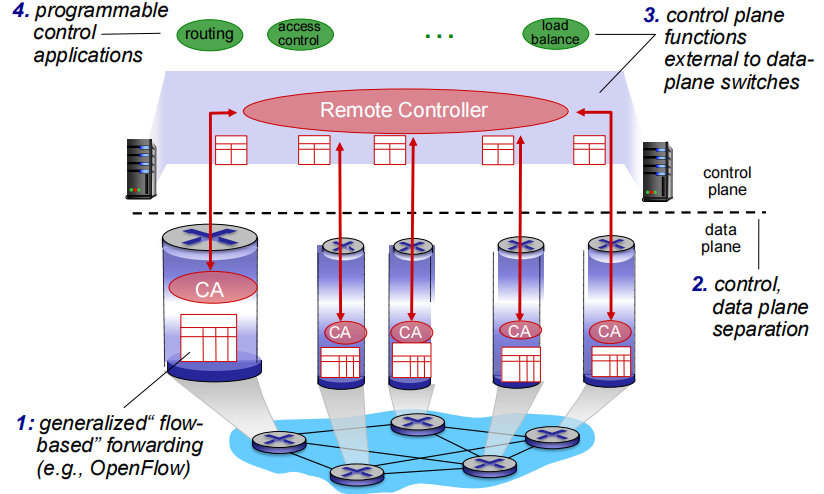
software-defined networking *(SDN) :*Logically centralized control plane
A distinct (typically remote) controller interacts with local control agents (CAs)
控制平面与数据平面分离,路由选择设备只执行转发,远程控制器计算并分发转发表
数据平面
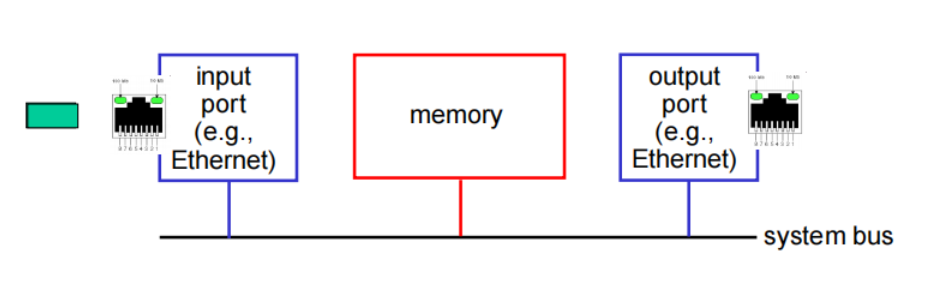
Router architecture overview
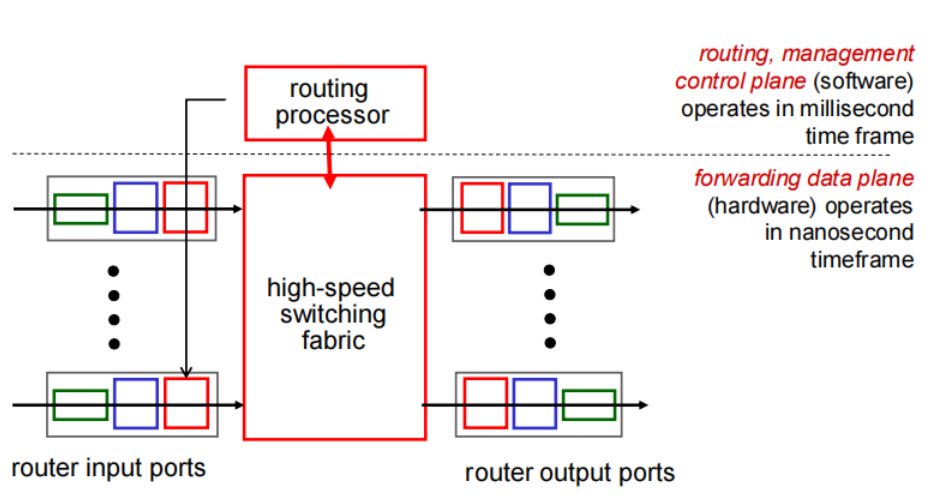
Input port functions
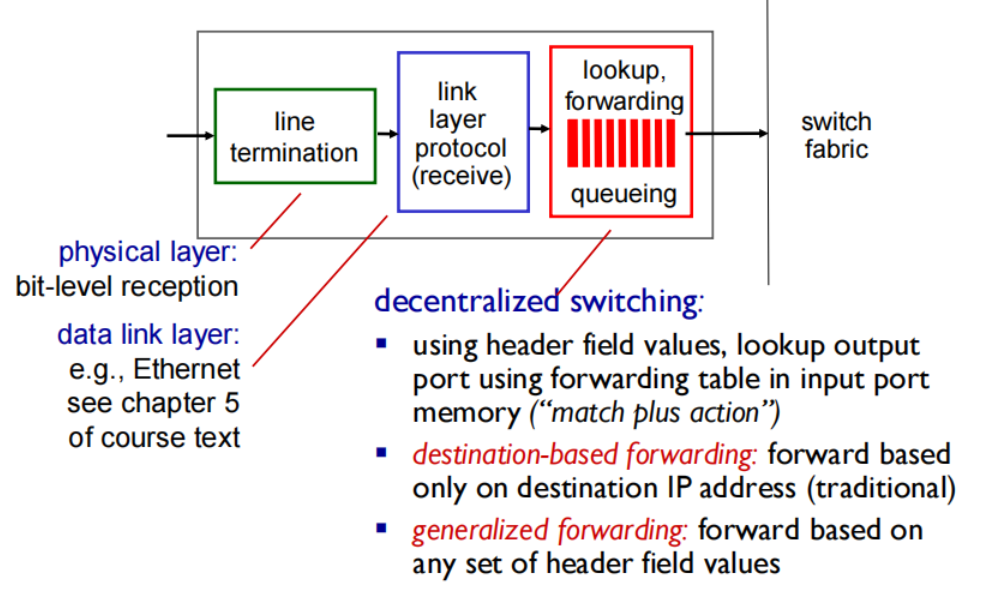
从左向右:分别实现物理层和链路层
decentralized switching*:*分布式交换(在此处使用转发表查找输出端口) 从总览图可以看到SDN控制器把转发表发送此处。
利用头部信息中的IP地址来查找输出段口有两种方法:
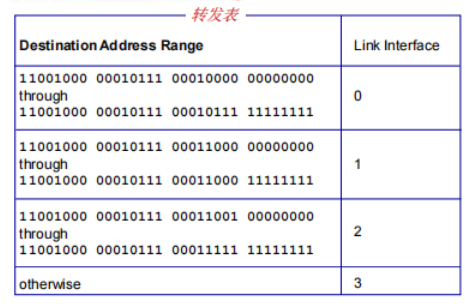
- destination-based forwarding 基于目标转发: 只是依赖于IP地址,判断区间来判断输出端口(有超过40亿种表项)
Longest prefix matching:最长前缀匹配
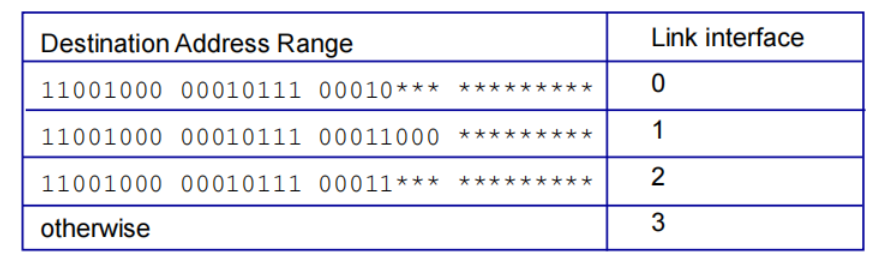
匹配IP中前面的字段,匹配成功则发送对应端口

选取最长的前缀作为匹配
often performed using ternary content addressable memories (TCAMs) specialised very high speed memory
content addressable: present address to TCAM: retrieve address in one clock cycle, regardless of table size
generalized forwarding 通用转发:
forward based on any set of header field values,不只依赖于IP做转发,诸多因素会影响其转发
Switching fabrics
transfer the packet from input buffer to appropriate output buffer
switching rate: rate at which packets can be transfer from inputs to outputs
• N inputs: switching rate N times line rate desirable
switch rate是 input rate的N倍(假如N个数据入口)
three types of switching fabrics
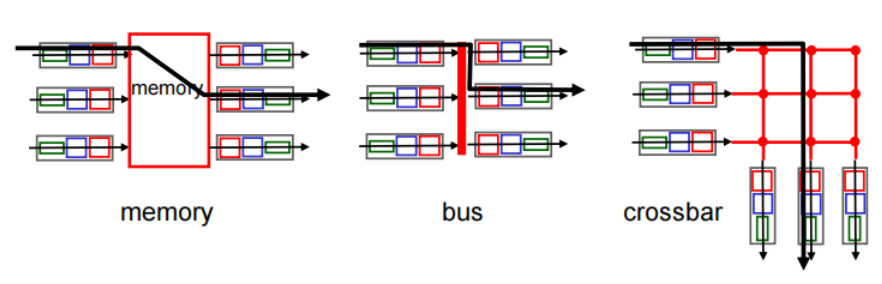
Switching via memory:内存交换
第一代路由器:本质为传统计算机 traditional computers with switching under direct control of CPU
packet copied to system’ s memory
speed limited by memory bandwidth (2 bus crossings per datagram数据报通过总线两次(读+写))
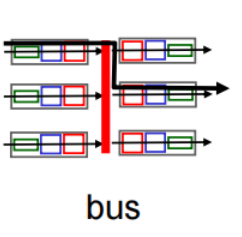
Switching via a bus: 总线交换
datagram from input port memory to output port memory via a shared bus
bus contention(总线竞争): switching speed limited by bus bandwidth
分组可以到达所有输出端口,但是只有端口号匹配的端口才能保存
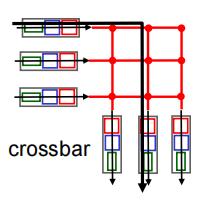
Switching via interconnection network :互联网络交换
overcome bus bandwidth limitations
advanced design: fragmenting datagram into fixed length cells, switch cells through the fabric.
可以并行转发多个分组(输出端口不一样时)
输出端口一致,仍要等待
Output ports
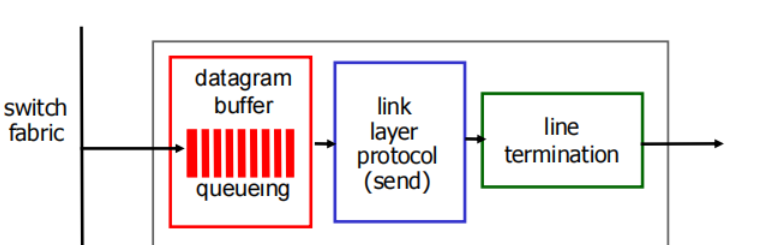
queue
Datagram (packets) can be lost due to congestion, lack of buffers
▪ buffering required when datagrams arrive from fabric faster than the transmission rate
▪ scheduling discipline chooses among queued datagrams for transmission调度规则来选择调度
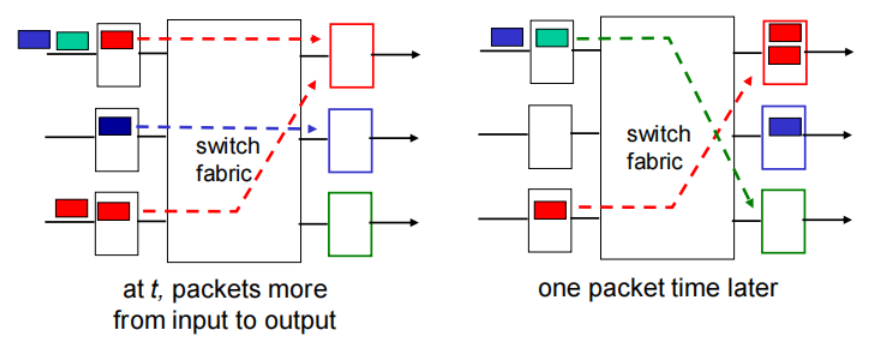
Input port queuing
switch rate slower than input ports combined -> queueing may occur at input queues
- queueing delay and loss due to input buffer overflow!
Head-of-the-Line (HOL) blocking 线路前部阻塞 : queued datagram at front of queue prevents others in queue from moving forward
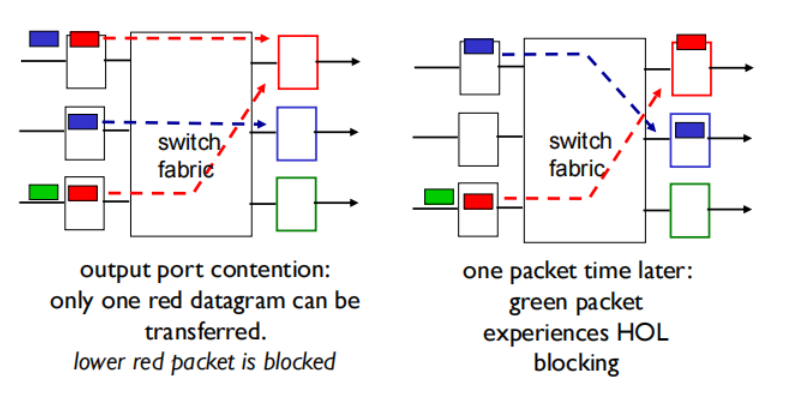
当下方红色块在排队等待上方红色块交换时,绿色块不得已地被阻塞了
Output port queueing
buffering when switch rate via switch exceeds output line speed
queueing (delay) and loss due to output port buffer overflow!
buffering equal to (N条TCP流对应的Buffer数量)
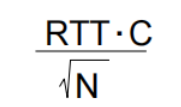
Scheduling mechanisms
调度机制:当分组到达输出端buffer时,选择某种mechanism将packets transmit到link
scheduling: choose next packet to send on link. 选哪一个packet输出
▪ FIFO scheduling – first in first out 先进先出
弃尾: If queue is full last packets are dropped.
▪ Priority scheduling 优先调度
Some packets are more important
会有一部分packet进入优先权队列
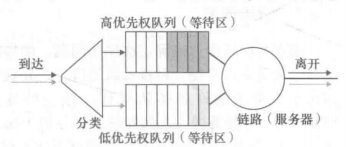
▪ Round robin scheduling 循环调度
• If your queue is from several inputs ports treat them fairly
• Pick a packet from input port 1, then 2, then 3, then 4
• Port that is sending lots of traffic doesn’t block others. 不会阻塞别的端口
• **Weighted Fair Queue加权公平排队 (like this but give some queues a little more priority – give a little more traffic(流量) to port 1) **可以给某个端口更多的加权
IP :Internet Protocol
IP datagram format
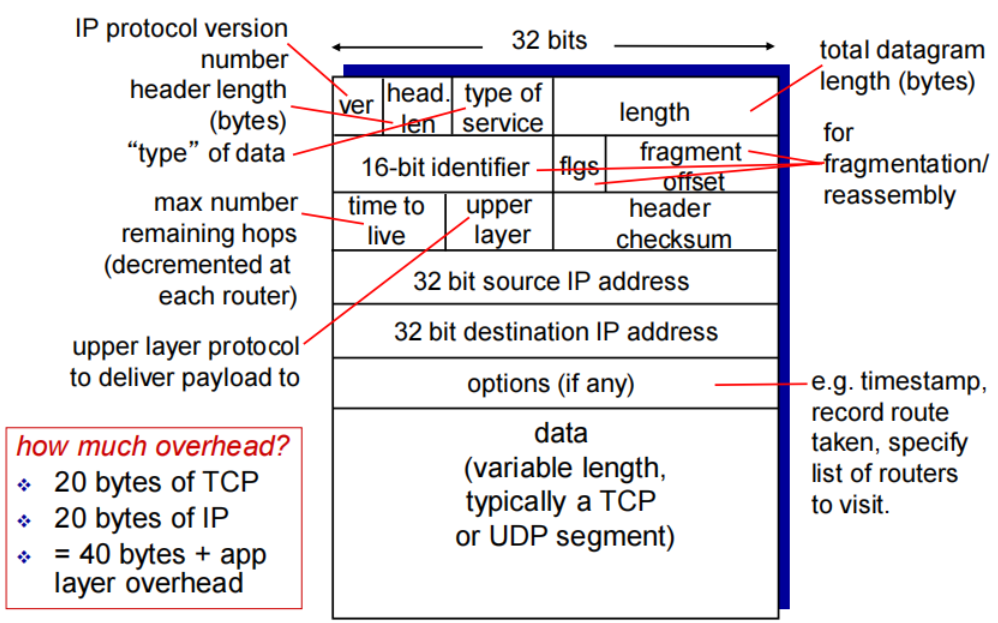
IP头部:20-60byte
overhead(开销):指头部

IP fragmentation, reassembly
数据报分片重组
network links have MTU(Maximum Transfer Unit ) (largest possible link-level frame)
链路层有MTU,且不同路由之间链路的MTU可能不同
MTU是链路层最大有效载荷(包括IP头部加IP信息)
large IP datagram divided (“fragmented”) within net
所以长的数据报可能无法装在MTU中,需要分片

• one datagram becomes several datagrams “reassembled” only at final destination
在目标主机重组
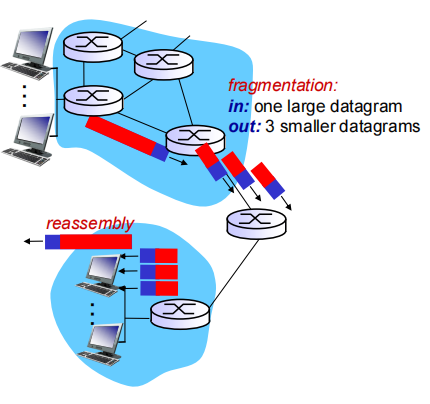
• IP header bits used to identify, and order related fragments
将标识、标志和片偏移字段放在数据报首部
为了让目的主机绝对地相信它已收到了 初始数据报的最后一个片,最后片的标志比特(fragflag)被设为0 、而所有其他片的标志比特被设为1,为了让目的主机确定是否丢失了片(且能按正础的顺序重新组装片)使用偏移字段(offset)指定该片应放在初始 IP 数据报的哪个位置(不算头部)
20byte header+1480 segment data
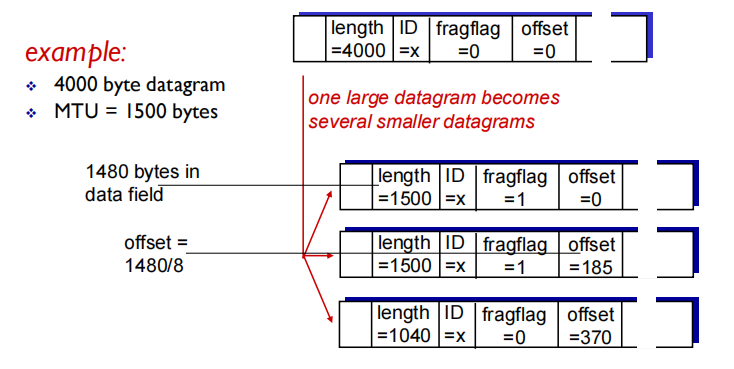
分片长度必须为8的整数倍:偏移量单位为8B
MTU=1500bytes只能装1480的数据,此外offset是指该片的初始(第一个data)应该放在最终组合起来的数据报中的哪个位置(不算header,以8B为单位)最后一个的offset肯定是第一个非0 offset的整数倍
exercise:
An IP packet has 4620 bytes in total of which 20 bytes are the IP header. It enters a network that has a Maximum Transfer Unit of 1900 bytes.

IPv4 addressing
introduction
IP address: 32-bit identifier for host, router interface
一个iP地址与一个接口相关联 associated with each interface,而不是与包括该接口的主机或路由器相关联
只有第三层的设备才有IP
- interface: connection between host/router and physical link(主机与物理链路之间的边界叫作接口)
- routers typically have multiple interfaces(实现转发)
- host typically has one or two interfaces IPv4 address notation(以太网+无线网)
每个 IP 址长度为 32 比特(等价为4字节),因 此总共有大约 40 亿个可能的 iP , 这些地址通常按所谓点分十进制记法(dotted-decimal notation)书写,即地址中的每个字节用它的十进制形式书写,各字间以句点隔开
There are three common notations to show an IPv4 address:
• binary notation
• dotted-decimal notation (most commonly used)
• hexadecimal notation
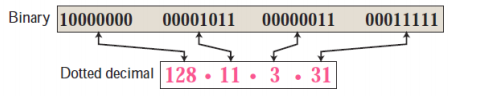
exercise:

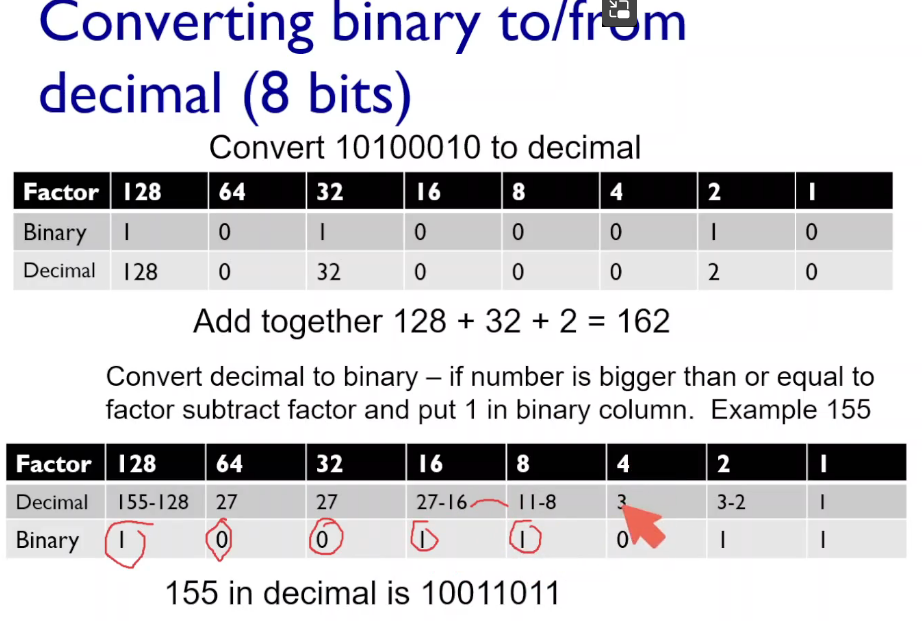
十进制转2进制
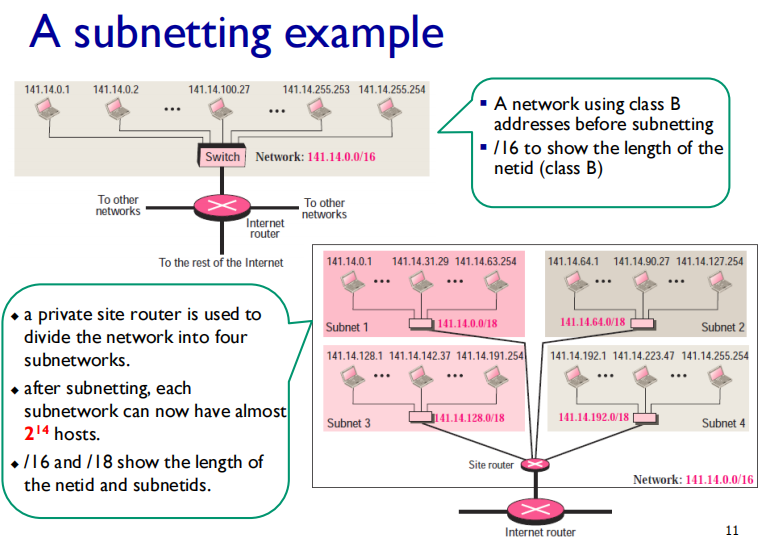
Subnets
ip地址为subnet part(网络)(高位)+host part(低位)
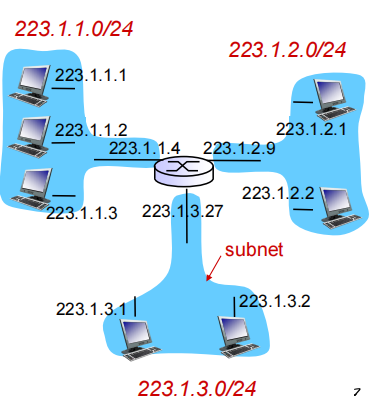
what’s a subnet ?
device interfaces with same subnet part of IP address
can physically reach each other without intervening router
to determine the subnets, detach each interface from its host or router, creating islands of isolated networks

图中有6个子网
subnet mask (or slash notation): number of bits taken to identify network
子网掩码的长度也是32位,左边是网络位,用二进制数字“1”表示,1的数目等于网络位的长度;右边是主机位,用二进制数字“0”表示,0的数目等于主机位的长度。
如:223.1.3.0/24 表示子网(子网位)部分有24位
• /8 size of old class A
• /16 size of class B
• /24 size of class C
Three-Level Addressing

例如,130.66.0.0是一个B类网络,它的主机位部分有两个字节。当借用此网络的第三个字节的高两位分配子网时,其可用的子网地址分别为130.66.2.0和130.66.3.0。
其中,130.66.2.216的网络地址为130.66.0.0,子网地址为130.66.2.0 主机位为216。(130.66.255.255、130.66.2.255不可作为host地址,是广播地址)
Network mask and subnetwork mask
Subnetting increases length of netid and decreases length of hostid.
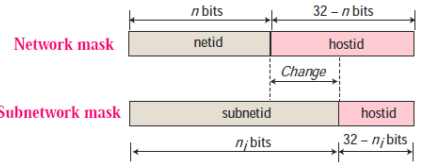
To divide a network to s number of subnetworks, each of equal numbers of hosts, the subnetid for each subnetwork can be calculated as
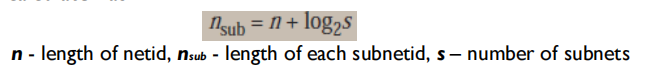
subnetid 包括 netid
Why subnetting ?
▪ The idea of splitting a block to smaller blocks is referred to as subnetting.
▪ In subnetting, a network is divided into several smaller subnetworks (subnets) with each subnetwork having its own subnetwork address
Classful IP addressing 分类编址
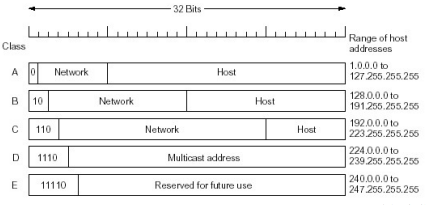
In classful addressing, the IP address space is divided into five classes: A, B, C, D, E.
Starting number, n (first byte), shows whether Class A, B or C
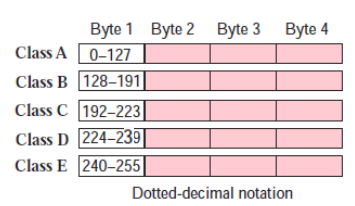
• Class A: n < 128 (($2^{24}-2$) hosts) 0
• Class B: 128 < n < 192 (($2^{16}-2$) hosts) 10
• Class C: 192 < n < 224 (($2^8-2$)hosts) 110
去除全0和全1地址(全0为网络地址,全1为广播地址)
These addresses are “special” and not used on the general Internet. You use them to set up test networks or networks of machines not accessible from outside.、

Classless addressing
In this architecture, the entire address space ($2^{32}$ addresses) is divided into blocks of different sizes.(可以任意分网络部分和主机部分,不用每8bit分一次,n可以等于0-32任何数)
slash notation : CIDR (Classless InterDomain Routing) notation.
For a /n address, the first n bits are the network address and the last 32-n bits are for the host.
▪ Example 129.66.25.5/22
- Network part (22 bits – because it is /22),Host part 10 bits(32 bits – 22 bits)
10000001.01000010.00011001.00000101
- Network address: 129.66.24.0/22
Network address is the address with all the host bits set to zero – address like any other but represents the network. Network address 也可以分给主机
10000001.01000010.00011000.00000000
- Broadcast address: 129.66.27.255/22
Broadcast address (sends to everyone) is the address with all the host bits set to one.
10000001.01000010.00011011.11111111

可以容纳2^m-1个主机

3个主机但是要去掉广播地址(网络地址可以用)
VLSM(variable length subnet mask)
使用VLSM为某个网络分配地址。最有效的利用现有的地址空间。
所谓VLSM,就是说每个子网的子网id可变,这样比较灵活。
Only classless routing protocols support VLSM
exercise:
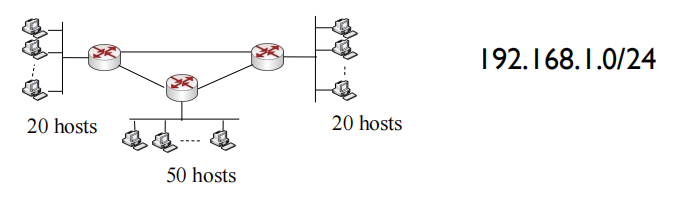
首先我们要知道整个网络能分配的ip有哪些。观察到题中给了192.168.1.0/24,可以知道前24位都不能分,后面8位都可以分。
start with the largest subnet to avoid waste,50(00110010)个host对应于 6bits (32<50<64),所以从后八位中取出前2位(后六位留给主机位)
192.168.1.0 - 192.168.1.63 (allocate to the largest subnet with 50 hosts: 192.168.1.0/26)
同理20=00010100 = 5 bits
Reserve 5 bits for hosts
192.168.1.0 – 192.168.1.63 (already allocated)
192.168.1.64 - 192.168.1.95 (allocate to the subnet with 20 hosts: 192.168.1.64/27)
192.168.1.96 – 192.168.1.127 (allocate to the other subnet with 20 hosts: 192.168.1.96/27)
为路由器(点到点)分配ip
/30 is commonly used for point-to-point WAN link/serial link between routers
2=00000010 = 2 bitsReserve 2 bits for hosts
192.168.1.128 -192.168.1.131 (allocated to link between routers: 192.168.1.128/30)
192.168.1.132 -192.168.1.135 (allocated to link between routers: 192.168.1.132/30)
192.168.1.136 -192.168.1.139 (allocated to link between routers: 192.168.1.136/30)
Only classless routing protocols support VLSM.
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
allow host to dynamically obtain its IP address from network server when it joins network
DHCP 许主机自动获取(被分配)IP 地址
• can renew its lease on address in use
• allows reuse of addresses (only hold address while connected/“ on ”)
• support for mobile users who want to join network (more shortly)
移动设备可以不用配置直接连接进网络
每个子网具有DHCP服务器,通过一个中继代理路由器与之相连
*DHCP :*新主机到达子网时的配置操作(这里配置的其实是私有网)
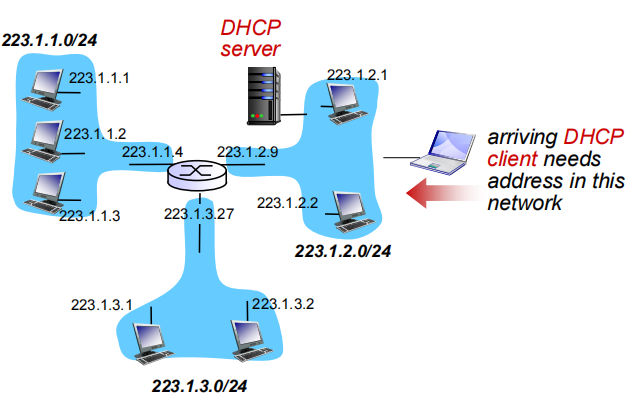
DHCP只在网络、子网中工作,因为broadcast只存在于子网中
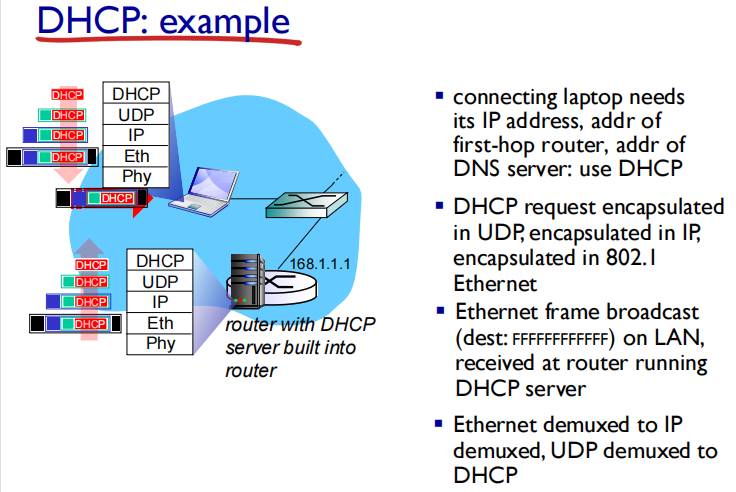
DHCP过程
host broadcasts “DHCP discover” msg [optional]
DHCP发现报文(客户端寻找DHCP服务器)此时使用源IP 0.0.0.0和广播目的地址255.255.255.255. 该子网中所有节点都接收到此message(包括DHCP)
DHCP server responds with “DHCP offer” msg [optional]
DHCP服务提供报文,向客户端做出响应:向255.255.255.255进行广播为它分配到的新加入主机的IP。
每个子网里有多个DHCP,经过DHCP discover 广播后,多个DHCP server都提供了IP
host requests IP address: “DHCP request” msg
客户端在接收到所有DHCP offer后选择一个想要的IP,并将这个IP对应的DHCPserver的IP地址封装成DHCP请求一起广播出去,对于该DHCP来说,意味着接收了它的IP。对于其他DHCP来说意味着拒绝了它的ip
注意此时还没完全分配IP,所以还是使用0.0.0.0
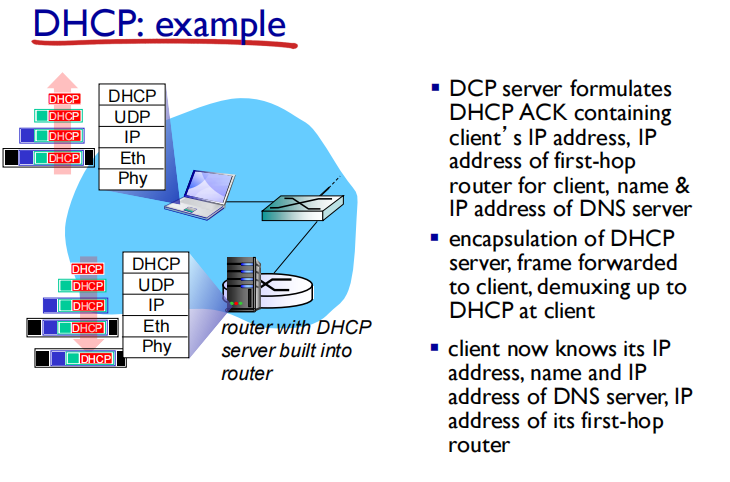
DHCP server sends address: “DHCP ack” msg
DHCP服务器确认请求(表示允许你用这个IP)
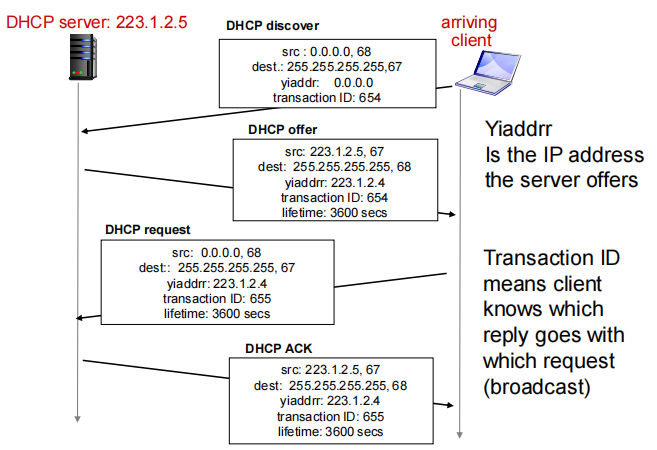
67 68是端口号(因为是UDP)
可以发现,DHCP 交互中,全程都是使⽤ UDP ⼴播通信
DHCP can return more than just allocated IP address on subnet:
• address of first-hop router for client(destination ip)
便于以后发消息时候可以找到第一跳路由
• name and IP address of DNS sever
• network mask (indicating network versus host portion of address)
DHCP基于UDP
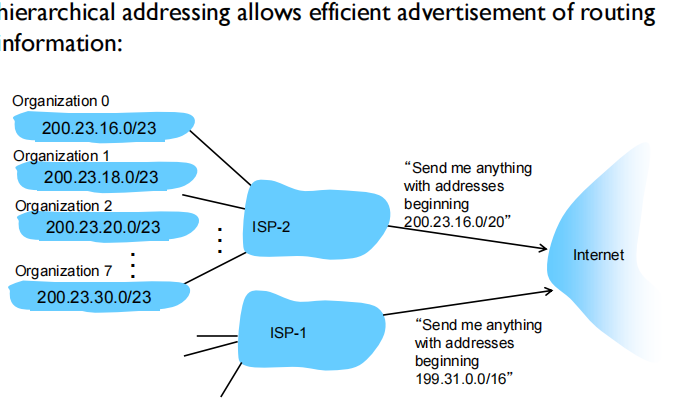
Hierarchical addressing
提高效率
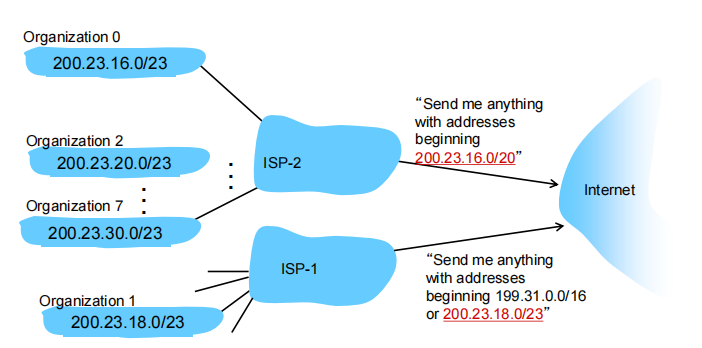
把organization1 转入isp1时ISP向Internet请求信息的子网地址多了一条信息
NAT: network address translation
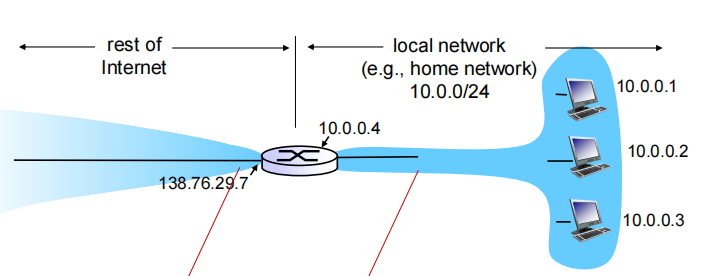
- 本地网络通过一个NAT router (一个IP地址)与外界联系
all datagrams leaving local network single source NAT IP address: 138.76.29.7, different source port numbers
- 专用地址:可以在子网中互发信息但是在外网看来,只有一个IP local network uses just one IP address
datagrams with source or destination in this network have 10.0.0/24 address for source, destination (as usual)
range of addresses not needed from ISP: just one IP address for all devices 这个地址不是由ISP划分的(是路由器中DCHP使用保留地址进行分配的:不是E类地址)
can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world在本地网络中更改,与外界无关
can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network
devices inside local net not explicitly addressable, visible by outside world (a security plus)
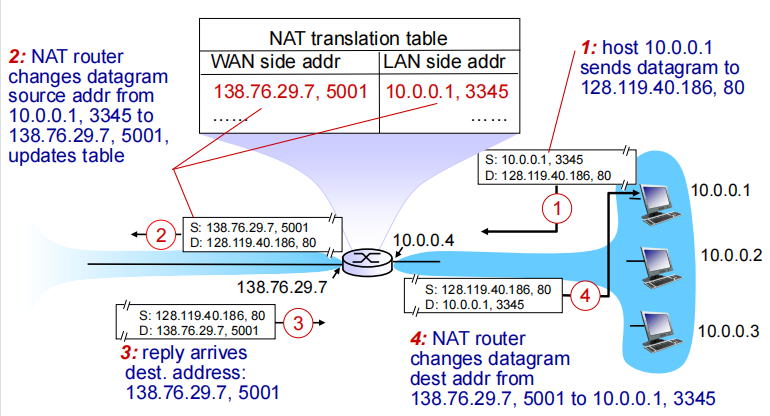
implementation
▪ outgoing datagrams: replace (source IP address, port #) of every outgoing datagram to (NAT IP address, new port #). . . remote clients/servers will respond using (NAT IP address, new port #) as destination addr
把LAN的源IP、端口替换为中NAT的IP和任意一个未在转换表中的端口
▪ remember (in NAT translation table) every (source IP address, port #) to (NAT IP address, new port #) translation pair
记录在NAT translation table
▪ incoming datagrams: replace (NAT IP address, new port #) indest fields of every incoming datagram with the corresponding (source IP address, port #) stored in NAT table
传回来的数据从NAT translate table中查询,转化为LAN地址和端口
16-bit port-number field 端口号字段为16bit:
• 60,000 simultaneous connections with a single LAN-side address!(可以支持超过60000个并行连接)
NAT几点争议:
routers should only process up to layer 3(但NAT router涉及到了port)
address shortage should be solved by IPv6
violates end-to-end argument (complexity should be at network “ends” not middle)
IPv6
32-bit address space be completely allocated(using 128 bit)
IPv6 datagram format:
fixed-length 40-byte header
no fragmentation allowed

IPv6 datagram format
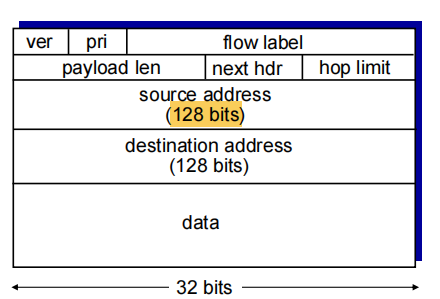
priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow
flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.”
next header: identify upper layer protocol for data
checksum: removed entirely to reduce processing time at each hop 和TCP,UDP重复 删掉了
options: allowed, but outside of header, indicated by “Next Header” field
变成下一个header
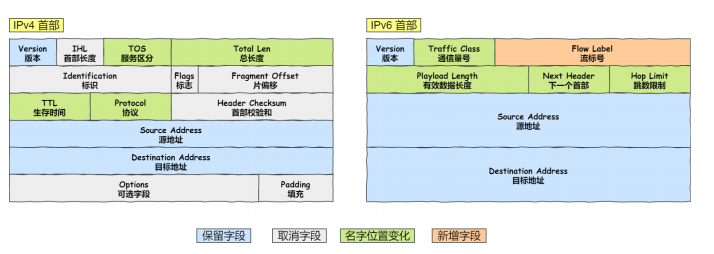
IPv6 相⽐ IPv4 的⾸部改进:取消了⾸部校验和字段。 因为在数据链路层和传输层都会校验,因此 IPv6 直接取消了 IP 的校验。
取消了分片重新组装相关字段。
取消选项字段。 选项字段不再是标准 IP ⾸部的⼀部分了,但它并没有消失,⽽是可能出现在 IPv6 ⾸部中的「下⼀个⾸部」指出的位置上。删除该选项字段使的 IPv6 的⾸部成为固定⻓度的 40 字节。
ICMPv6: new version of ICMP (see later lecture)
• additional message types, e.g. “Packet Too Big”
• multicast group management functions
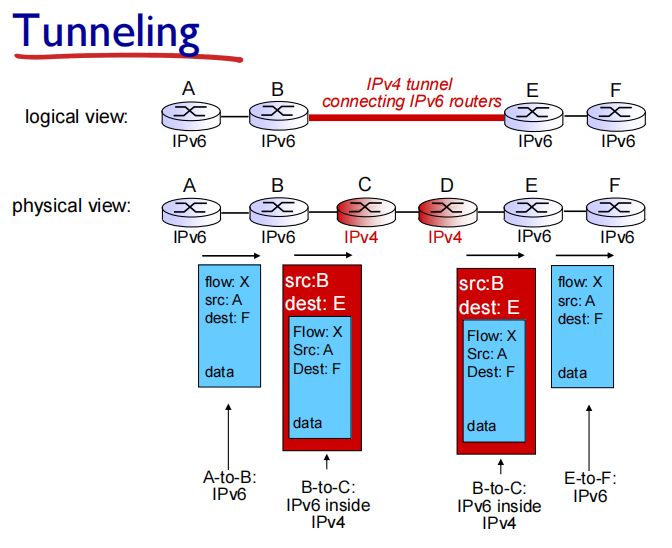
Transition from IPv4 to IPv6
not all routers can be upgraded simultaneously 路由器内部封装的协议是IPv4,无法同时把世界上的router全upgrade

tunneling: IPv6 datagram carried as payload in IPv4 datagram among IPv4 routers
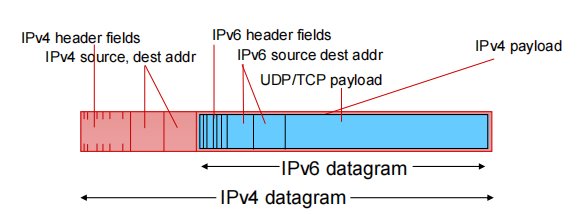
ipv4数据报中的载荷是ipv6的全部数据报
IPv6 and IPv4
Generalized Forward and SDN
SDN allows more flexibility in the control and data plane.
• Program your own control algorithms in language you know (Java, python etc).
• Forwarding can use any part of the packet header.
• Not a distributed system, but a single centralised control point.
• Programmable, not fixed – you can program the controller in a high-level language that you know.
• Create your own algorithms and test them on the network without spending a million dollars to create a new hardware router.
OpenFlow data plane
OpenFlow is a specific SDN protocol,帮助沟通控制平面和数据平面
flow: defined by header fields
generalized forwarding: simple packet-handling rules
match+action: different kinds of devices become one 集合这些设备的功能
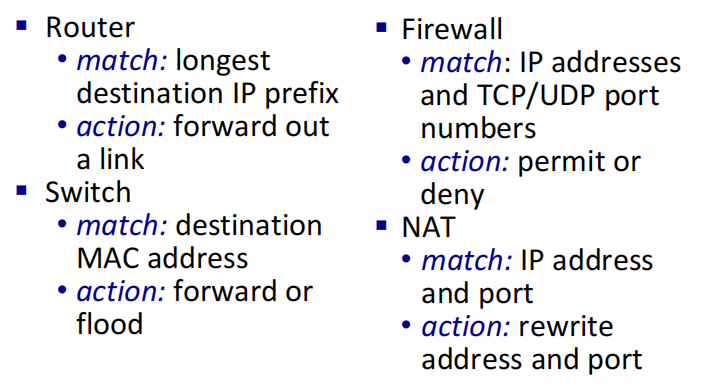
通用转发的例子
Flow Table Entries
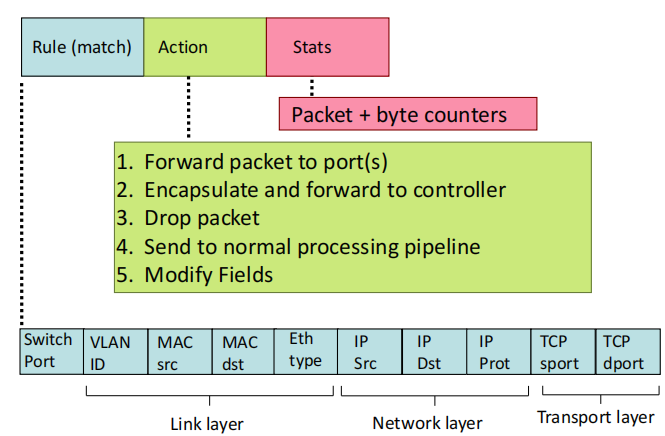
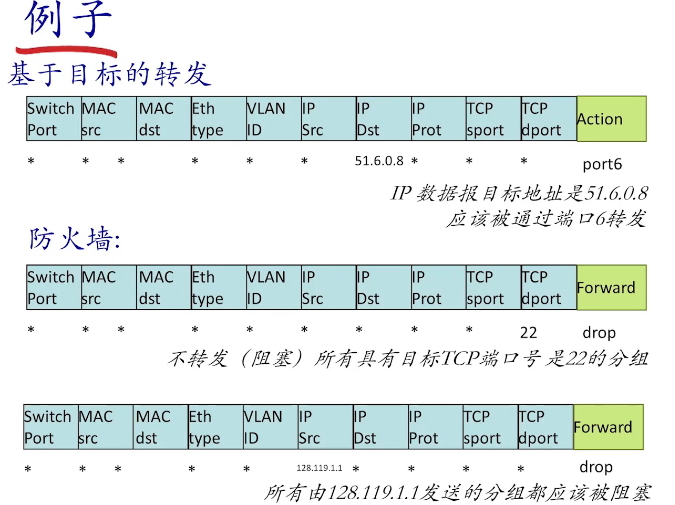
分组头部与流表不同字段匹配实现不同功能
通用转发:并不是和基于目标转发一样只识别IP地址进行转发,而是整合了网络中各个层次的网络配置信息,由一些关键字和执行动作组成的灵活规则。
当OpenFlow交换机收到一个数据包,将包头解析后与流表中流表项的匹配域进行匹配,匹配成功则执行指令
Control Plane
data plane: forwarding: move packets from router’s input to appropriate router output
control plane: routing: determine route taken by packets from source to destination
Routing protocols
Routing protocol goal: determine “good” paths (equivalently, routes), from sending hosts to receiving host, through network of routers 从发送方到接收方的过程中确定一条好路径
▪ path: sequence of routers packets will traverse in going from given initial source host to given final destination host
Graph abstraction of the network
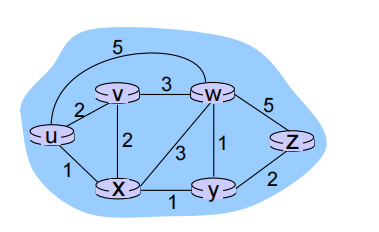
graph: G = (N,E) N个节点E条边的集合
N = set of routers = { u, v, w, x, y, z }
E = set of links ={ (u,v), (u,x), (u,w), (v,x), (v,w), (x,w), (x,y), (w,y), (w,z), (y,z) }
c(x,x’) = cost of link (x,x’) 每个连接上的开销
cost could always be 1, or inversely related to bandwidth,or inversely related to congestion
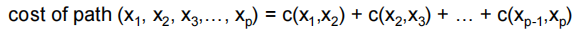
routing algorithm: algorithm that finds that least cost path
Routing algorithm classification
global or decentralized information
global:
▪ all routers have complete topology, link cost info
▪ “link state” algorithms
decentralized:
▪ router knows physically-connected neighbors, link costs to neighbors
▪ iterative process of computation, exchange of info with neighbors
走一步看一步
▪ “distance vector” algorithms
static or dynamic
static:
▪ routes change slowly over time路由随时间变化非常缓慢
dynamic:
▪ routes change more quickly
周期性变化
• periodic update
• in response to link cost changes
A link-state routing algorithm:Dijkstra’s algorithm
链路状态路由选择算法,是集中式路由算法
Dijkstra’s algorithm
via “link state broadcast” known net topology, link costs to all nodes
在开启算法之前,提前通过广播知道每个连接的开销
after k iterations, know least cost path to k dest.’ s
c(x,y): link cost from node x to y; = ∞ if not direct neighbors
D(v): current value of cost of path from source to dest. v
源节点到v的最低开销
p(v): predecessor node along path from source to v
前序节点
N’: set of nodes whose least cost path definitively known
最小开销已经明确了的节点的集合
1 Initialization:
2 N' = {u}
3 for all nodes v
4 if v adjacent to u
5 then D(v) = c(u,v)
6 else D(v) = ∞
7
8 Loop
9 find w not in N' such that D(w) is a minimum
10 add w to N'
11 update D(v) for all v adjacent to w and not in N' :
12 D(v) = min( D(v), D(w) + c(w,v) )
13 /* new cost to v is either old cost to v or known shortest path cost to w plus cost from w to v */
14 until all nodes in N'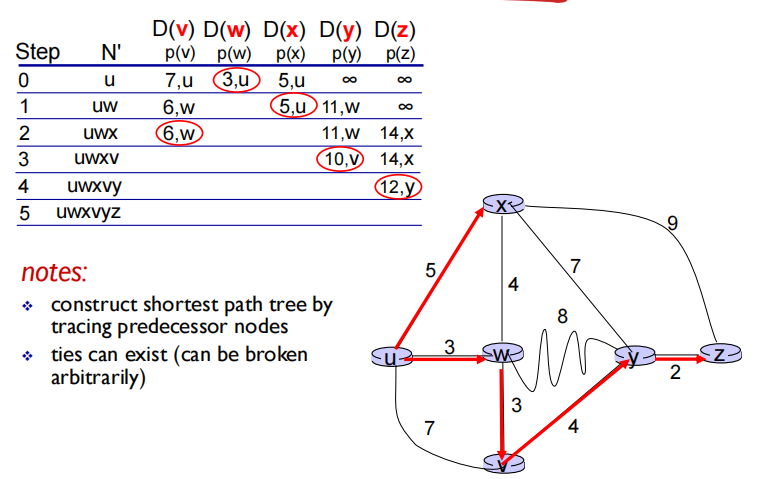
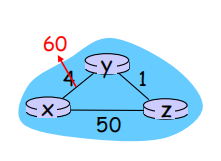
画圈:首先N’中只有u,现在找与其相连边中开销最小的作为路径如图(u,w),此时N’中有u和w,找与这两个节点相邻,并且到u开销最小的:如图为x………如此循环直到到达目标节点。当LS算法结束时,我们发现对于每个节点我们都能找到到它的最短路径
- shortest-path tree from u:
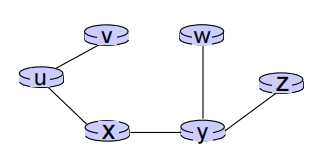
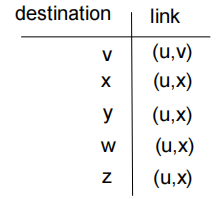
- forwarding table in u:
algorithm complexity:
n nodes(不算源节点) 最坏情况迭代次数为 n(n+1)/2 comparisons: O(n2 )
oscillations possible:
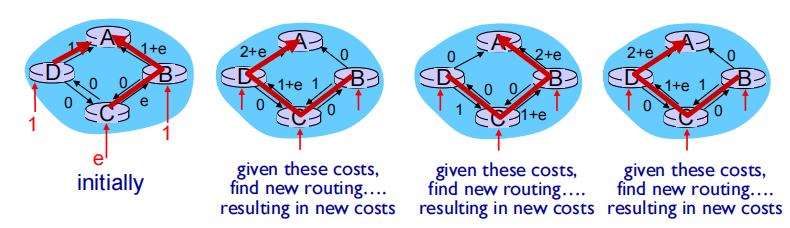
support link cost equals amount of carried traffic: 以流量为负载的情况
初始路由是B逆时针发送1个单位给A,D顺时针发送1个单位给A,C逆时针发送e个单位给B,B再给A
当再次运行LS算法之后,B、C、D路由都将会认为顺时针路由费用最低
再次运行LS算法,B、C、D路由器又将会向逆时针方向交付分组
产生选择震荡
(顺时针流量小拥堵时候,所有包都被路由表引导到逆时针,运行一会后,逆时针又会产生拥堵,所有包又被引导回顺时针)
Distance vector algorithm
距离向量算法是一种分散式路由算法,路由器不需要知道所有信息,只需要知道相邻路由的开销即可工作。然后通过迭代与相邻节点进行数据交换。
Bellman-Ford equation (dynamic programming)
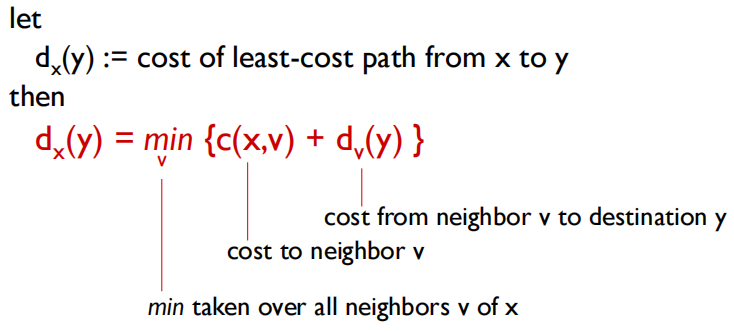
x到y的最小开销为:x到所有neighbor的开销加这个邻居到y的开销的和的最小值
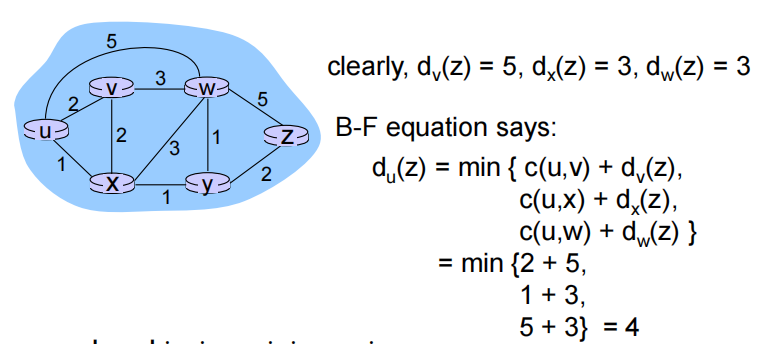

用距离向量Dx估计到所有点的距离
▪ node x:
• knows cost to each neighbor v: c(x,v)
• maintains its neighbors’ distance vectors(X的neighbor的位置向量). For each neighbor v, x maintains 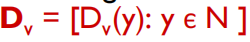
DV characters
- iterative, asynchronous:
local iteration caused by local link cost change,Then DV update message from neighbor
- distributed:
each node notifies neighbors only when its DV changes
from time-to-time, each node sends its own distance vector estimate to neighbors
when x receives new DV estimate from neighbor, it updates its own DV using B-F eq
每个节点不时的向邻居发送距离向量,如果x的distance vector因为bellman-ford方程发生改变,节点x将会向每个邻居发送更新后的距离向量,这继而让所有neighbor都更新自己的距离向量。
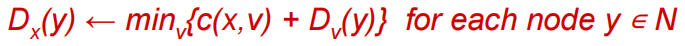
the estimate Dx (y) converge to the actual least cost dx (y)最终收敛到实际最短开销
DV process
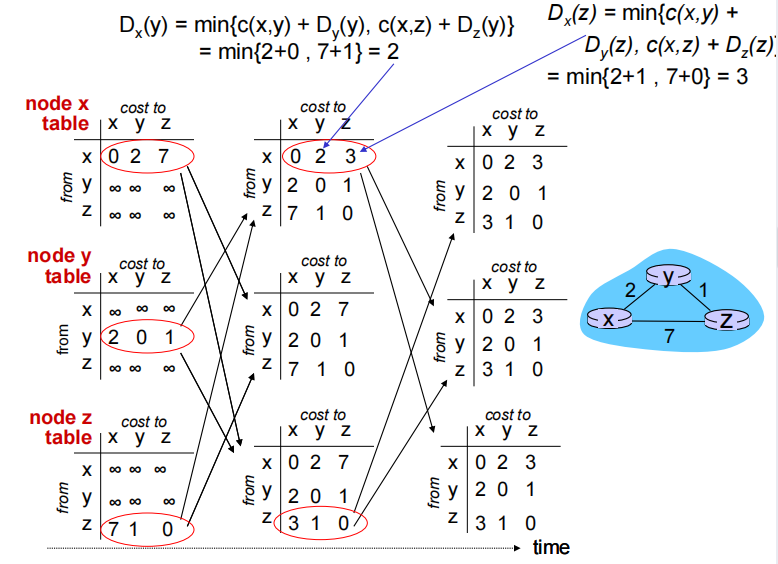
第一列的三个表是初始化的路由表,所以并没有上一个状态的邻居的距离向量(初始化为∞)。初始化后,每个节点向它的两个邻居发送距离向量(每个表中一行为一个距离向量),而在第二列表中由于距离向量更新,所以要按照bellman-ford公式重新计算路由表(计算过程看上图),而后由于y的距离向量在三张表里相同,所以并不发送,而xz会发送新值。最终无更新报文发送,则该算法达到了停止态。
link cost changes
❖ node detects local link cost change
❖ updates routing info, recalculates distance vector
❖ if DV changes, notify neighbors
开销减少的情况
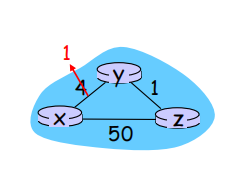
t0 : y detects link-cost change, updates its DV, informs its neighbors.
t1 : z receives update from y, updates its table, computes new least cost to x , sends its neighbors its DV.
t2 : y receives z ’s update, updates its distance table. y ’ s least costs do not change, so y does not send a message to z. 此时进入静止态。
开销减少的好消息在网络中迅速传播
开销增多的情况
开销增多的坏消息在网络中缓慢传播
❖ node detects local link cost change
❖ bad news travels slow - “ count to infinity” problem!(路由选择环路)
❖ 44 iterations before algorithm stabilizes ???
解决方法:*poisoned reverse:*(毒性逆转)
❖ If Z routes through Y to get to X :
▪ Z tells Y its (Z’s) distance to X is infinite (so Y won’ t route to X via Z)
Z告诉Y:经过y到x的距离向量无穷大
综上:LS :source router需要全局的信息,而DV中每一个router只需要与邻居进行通信,neighbor会告诉它neighbor 已知的信息
intra-AS routing in the Internet
现实中的路由器并不完全相同,而且拥有上亿(billions )的规模,can ’t store all destinations in routing tables,永远无法收敛。
此外由于英特网是ISP的网络,每个ISP都want to control routing in its own network
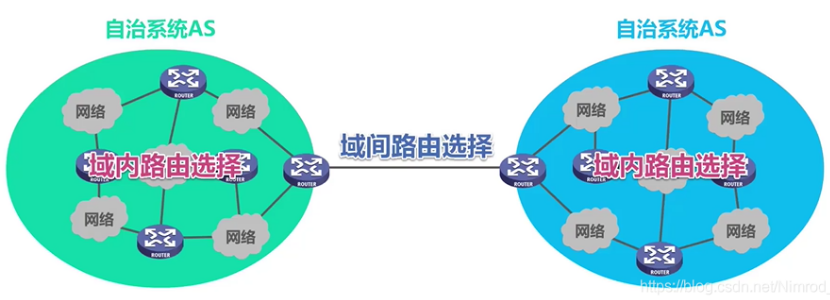
autonomous systems(AS)
aggregate routers into regions
intra-AS routing 域内路由选择
将一个ISP的路由器和它们之间的链路聚合成一个AS,相同AS中路由器运行着相同的路由选择算法(all routers in AS must run same intra-domain protocol)
- gateway router: at “edge” of its own AS, has link(s) to router(s) in other AS’es
inter-AS routing 域间路由选择
gateways perform inter-domain routing
forwarding table configured by both intra and inter-AS routing algorithm
自治系统内部和自治系统外部,分别采用不同类别的路由选择协议,分别进行路由选择
intra-AS routing determine entries for destinations within AS
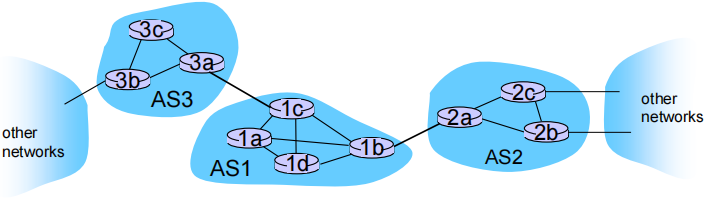
suppose router in AS1receives datagram destined outside of AS1
AS1接收到其他AS中发来的datagram,它需要发到gateway router,必须知道目的地的是否可到达,同时把这个datagram的可传达性传达给别的AS,这个工作是由inter- AS routing负责
router should forward packet to gateway router, but which one?
内部网关使用的协议:interior gateway protocols (IGP)
外部网关使用的协议:Border Gateway Protocol(BGP)
Intra-AS Routing:OSPF
most common intra-AS routing protocols:
• RIP: Routing Information Protocol 适合路由数量较少
• OSPF: Open Shortest Path First
• IGRP: Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
open指 publicly available公众可用
link-state algorithm 使用LS
route computation using Dijkstra’s algorithm,一台路由器构建整个AS的完整topology
router floods(泛洪) OSPF link-state advertisements to all other routers in entire AS
像所有路由器广播状态信息,每有一个链路变化,就泛洪一次,即使没状态变化也周期性泛洪
carried in OSPF messages directly over IP
features
security: all OSPF messages authenticated 所有信息需要授权(to prevent intrusion)
multiple same-cost paths allowed (only one path in RIP)
如果多条路开销一致,可以多路并行,分担开销
integrated uni- and multi-cast support 对单播和多播综合支持
Multicast OSPF (MOSPF) uses same topology data base as OSPF
hierarchical 支持层次结构
Internet inter-AS routing: BGP
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) 边界网关协议(每个AS统一的协议)
autonomous system 间的协议
将互联网中的ISP(glue)粘合在一起
使用DV算法,告诉路由器路径
BGP provides each AS a means to:
• eBGP 外部BGP: 连接不同AS之间的链路
obtain subnet reachability information from neighboring ASes (从相邻的ASes那里获得子网可达信息) 告诉别的子网”我在那”,接收到所有子网的”我在那”
• iBGP 内部BGP: 一个AS内部的BGP链路
propagate reachability information to all AS internal routers.(将获得的子网可达信息传遍到AS内部的所有路由器)
BGP选择一条最好的路径去其他AS,基于reachability information and policy
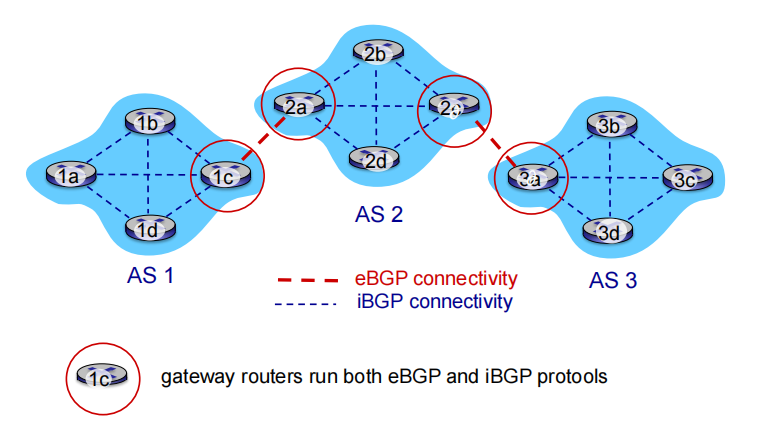
BGP session: two BGP routers (“ peers ”) exchange BGP messages over semi-permanent TCP connection: 两个BGP router通过半永久TCP交换路由选择信息
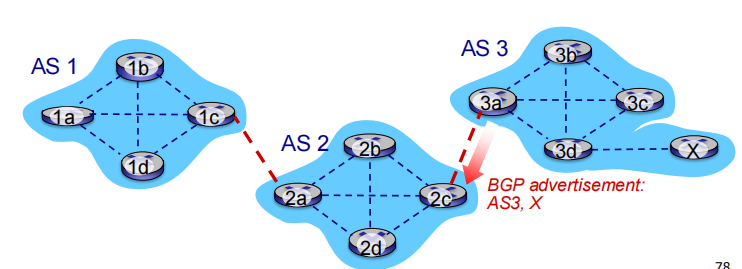
向AS1 AS2通告前缀x的可达性信息
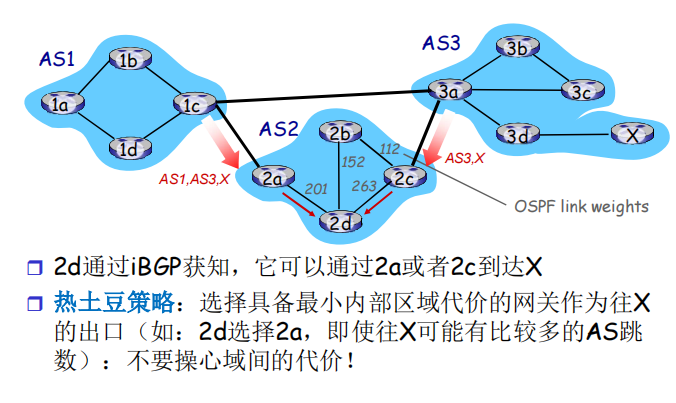
when AS3 gateway router 3a advertises path AS3 ,X to AS2 gateway router 2c
由于3a 参与AS3内所有路由运算,所有3a可以收集所有路由可达信息,并一起发给2c,相当于3a向2c承诺说 你可以通过我到达x
Path attributes and BGP routes
为了在多条路径中选择下一条,BGP在prefix里加入BGP attributes
prefix + attributes = “route” 前缀加属性=路由
- two important attributes:
• AS-PATH: list of ASes through which prefix advertisement has passed 记录前缀通过了的AS,每通过一个AS,向列表中记录一个
• NEXT-HOP: indicates specific internal-AS router to next hop AS
如当路由为AS2 AS3 x,Nest hop为2a左侧接口的IP地址
Policy-based routing:
gateway receiving route advertisement uses import policy to accept/decline path
当一个网关路由器接收到了一个路由通告, 使用输入策略来接受或过滤
过滤原因例1:不想经过某个AS,转发某些前缀的分组
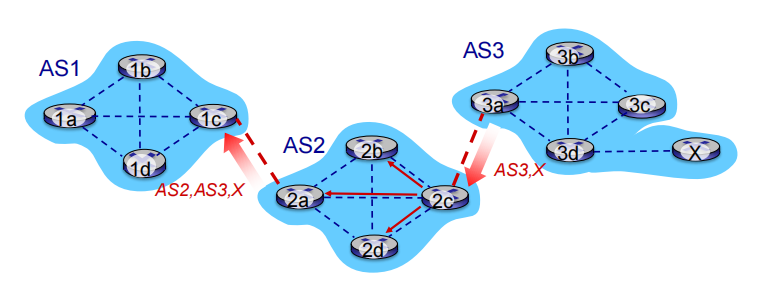
AS2 router 2c receives path advertisement AS3,X (via eBGP) from AS3 router 3a
Based on AS2 policy, AS2 router 2c accepts path AS3,X, propagates (via iBGP) to all AS2 routers
Based on AS2 policy, AS2 router 2a advertises (via eBGP) path AS2, AS3, X to AS1 router 1c
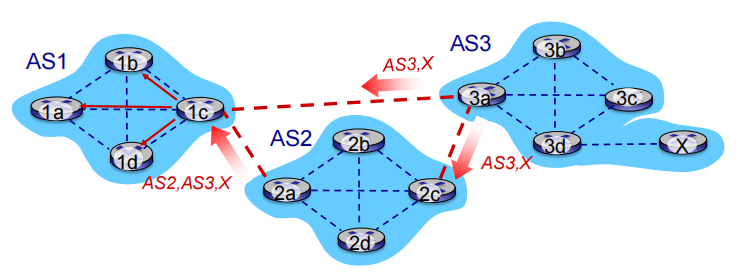
另一种policy:绕开AS2
▪ Based on policy, AS1 gateway router 1c chooses path AS3,X, and advertises path within AS1 via iBGP
BGP route selection
▪ router may learn about more than one route to destination AS, selects route based on:
local preference value attribute: policy decision
shortest AS-PATH
closest NEXT-HOP router: hot potato routing
additional criteria
SDN
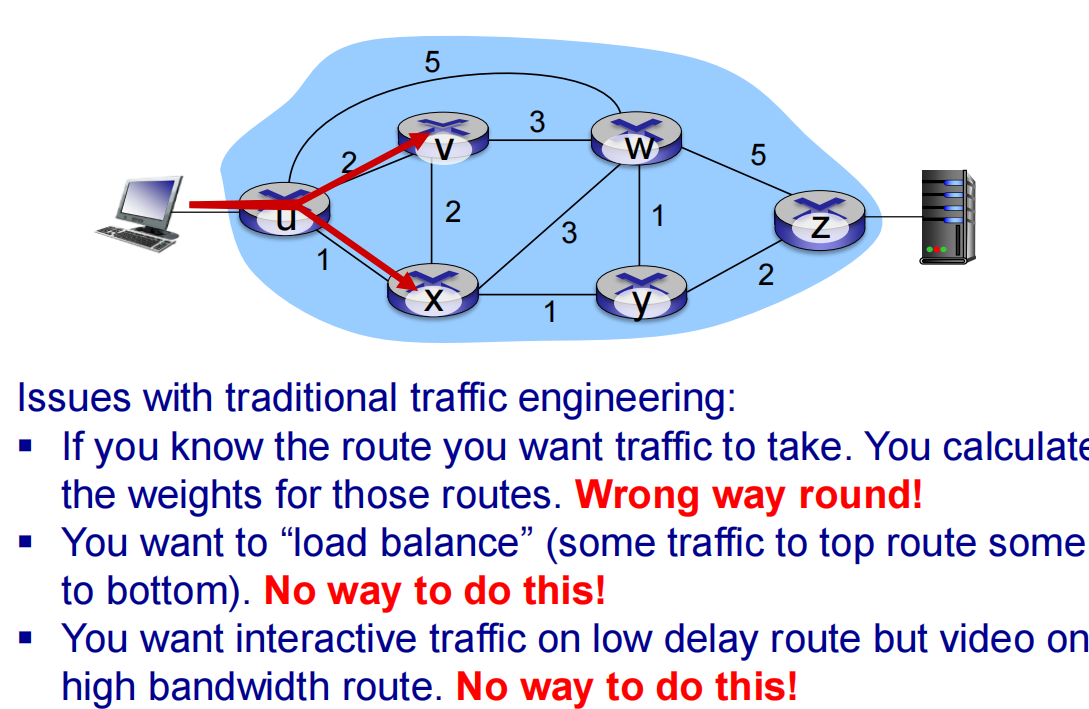
easier network management: avoid router misconfigurations, greater flexibility of traffic flows
传统per-router control plane无法解决的问题:
SDN特点
通用“ flowbased” 基于流的匹配+行动
可编程控制应用在控制器之上以网络应用形式实现各种网络功能
The control plane is “logically” centralised (it seems as if there is just one controller though there may be several for redundancy)
SDN结构
Data plane switches
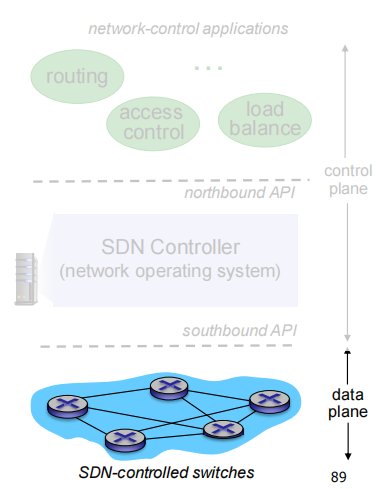
fast, simple, commodity switches implementing generalized data-plane forwarding in hardware
API for table-based switch control
基于南向API(例如OpenFlow),SDN控制器访问基于流的交换机
SDN controller (network OS):
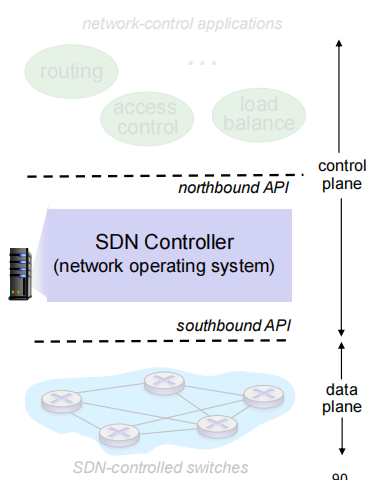
interacts with network control applications “above” via northbound API
通过上面的北向API和网络控制应用交互
interacts with network switches “below” via southbound API
通过下面的南向API和网络交换机交互
southbound protocol –connects controller to switch
northbound protocol –connects controller to apps
network-control apps
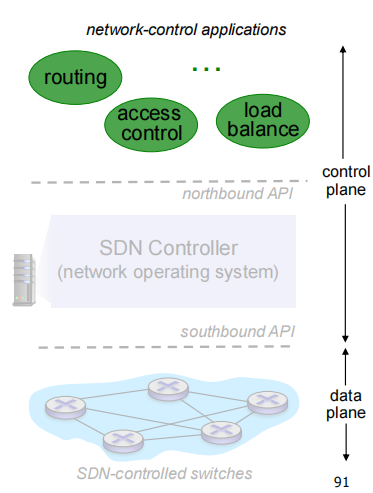
implement control functions using lower-level services, API provided by SDN controller
采用下层提供的服务(SDN控制器提供的API),实现网络功能
OpenFlow protocol
运行在SDN controller switch 之间,基于TCP
SDN: control/data plane interaction example
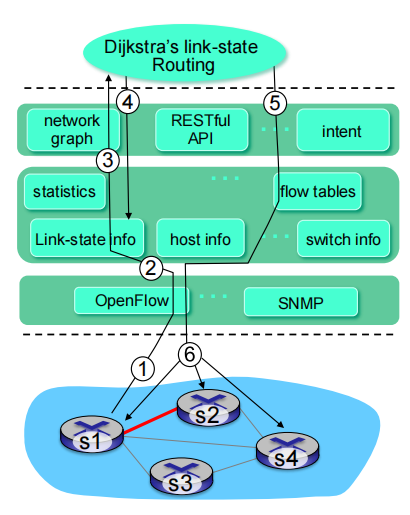
S1, experiencing link failure using OpenFlow port status message to notify controller
假设s1 s2之间端口,采用OpenFlow报文通告控制器
SDN 控制器接收OpenFlow报文,更新链路状态信息
Dijkstra路由算法应用被调用
Dijkstra路由算法访问控制器中的网络拓扑信息,链路状态信息计算新路由
链路状态路由app和SDN控制器中流表计算元件交互,计算出新的所需流表
控制器采用OpenFlow在交换机上安装新的需要更新的流表
ICMP: internet control message protocol
used by hosts & routers to communicate network-level information
最典型的用途是差错报告
- ICMP 的第一个功能是确认 IP 包是否能够成功到达目标地址,当两个设备通过互联网相连时,任意一个设备发送给另一个设备的 IP 包如果没有到达,就会生成 ICMP 数据包发送给设备共享。
- ICMP 的第二个功能是进行
网络诊断,经常使用 ICMP 数据包的两个终端程序是ping和traceroute,traceroute 程序用于显示两台互联网设备之间可能的路径并测量数据包在 IP 网络上的时延。ping 程序是 traceroute 的简化版本,我们经常使用 ping 命令来测试两台设备之间是否互联,ping 通常用来测试两台主机之间的连接速度,并准确报告数据包到达目的地并返回后所花费的时间。
network-layer “above” IP: 位于IP之上
• ICMP msgs carried in IP datagrams其msgs包含在IP数据头中
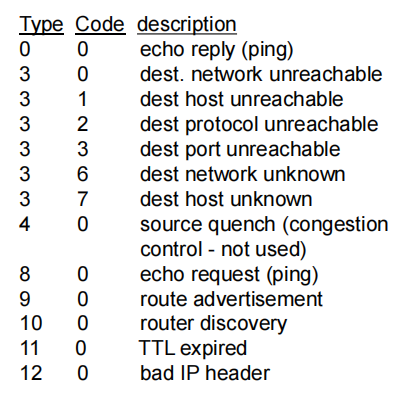
- ICMP message: type, code plus first 8 bytes of IP datagram causing error
ICMP报文中包含一类型字段一个编码字段,以及引起该ICMP报文首次生成的IP数据报的首部和前八个字节
http中一些状态码就是基于ICMP
ICMP报文类型:
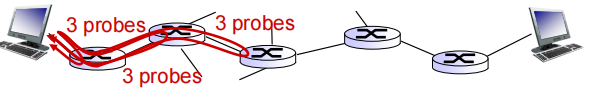
Traceroute and ICMP
通过发送探测报文来获取链路地址信息。第一个探测报文TTL为1,到达第一个路由器时,TTL减1为0所以丢掉这个探测包,同时向源主机发回ICMP时间超过报文,这时源主机就获得了第一个路由器的IP地址;接着源主机发送第二个探测报文,TTL增1为2,到达第一个路由器TTL减1为1并转发探测包到第二个路由器,这时TTL减1为0,丢掉这个探测包并向源主机发回ICMP时间超过报文,源主机就获得了第二个路由器的IP地址;以此类推,直到探测报文到达traceroute的目的地,这时源主机就获得了到目的地的每一跳路由的IP地址
source sends series of UDP segments to destination 源主机发送一系列不可达的UDP报文段,并且设置第一个数据报RTT为1 第二个为2……主机也为数据报启动定时器
when datagram in nth set arrives to nth route, router discards datagram and sends source ICMP message (type 11, code 0) router丢弃数据报后,返回ICMP警告给源主机,这个报文包括 name of router & IP address.
when ICMP message arrives, source records RTTs.当这个ICMP message到达源主机,源主机记录RTT,记录第n台路由器的IP和名字
stopping criteria(停止条件):
▪ UDP segment eventually arrives at destination host
▪ destination returns ICMP “port unreachable”message (type 3, code 3)
▪ source stops