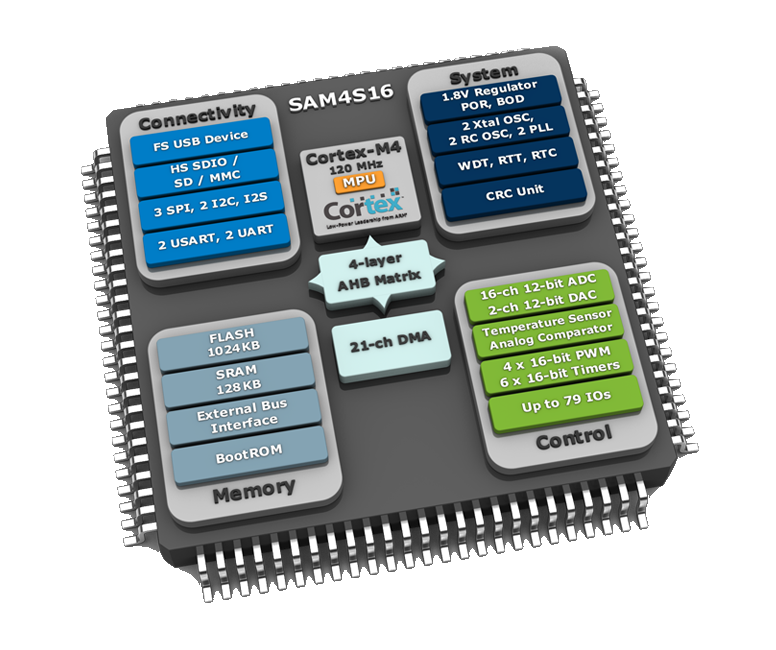
04-Intertupt
Exceptions and Interrupts
Interrupt or Exception Processing Sequence
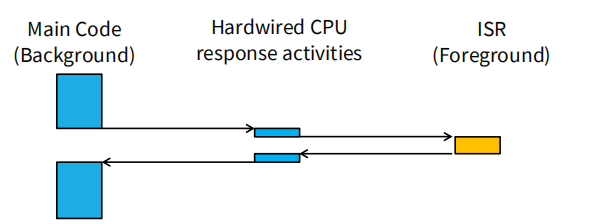
• Other code (background) is running.
• Interrupt trigger occurs.
• Processor does some hard-wired processing
• Processor executes the ISR (foreground), including the
return-from-interrupt instruction at the end.
• Processor resumes other code.
中断服务程序(Interrupt Service Routine)

• Hardware-triggered(硬件触发) asynchronous software routine
• Triggered by hardware signal from peripheral or external device
• Asynchronous - can happen anywhere in the program (unless interrupt is disabled)
• Interrupt service routine runs in response to the interrupt
微控制器的基本原理
•提供高效的基于事件的处理,而不是轮询
•提供对事件的快速响应,无论程序状态,复杂性,位置
•允许许多多线程嵌入式系统在没有操作系统的情况下进行响应
Entering Exception Handler
进入异常处理

在异常处理开始前,MSP或PSP的数值会相应地被自动调整。PC也会被更新为异常处理的起始地址,而链接寄存器(LR)则会被更新为名为EXCRETURN的特殊值。该数值为32位,且高27位为1。低5位中有些部分用于保存异常流程的状态信息(如压栈时使用的哪个栈)。该数值用于异常返回。
一旦产生异常,微处理器
– 首先现场保护
• 将当前R0‐R3、R12、LR、PC、xPSR压入当前栈中
– 接着读取异常向量
• 根据异常的类型号n,计算出异常处理程序的入口地址(也称为异常向量)的存放偏移地址n*4,将该地址处的一个字读出。
– 将LR置为EXC_RETURN,将读取的异常向量值加载至PC。
1. Finish Current Instruction
Most instructions are short and finish quickly
Some instructions may take many cycles to execute
Load Multiple (LDM), Store Multiple (STM), Push, Pop, MULS (32 cycles for some CPU core implementations) 延迟中断响应
If one of these is executing when the interrupt is requested, the processor:
• abandons the instruction
• responds to the interrupt
• executes the ISR
• returns from interrupt
• restarts the abandoned instruction
2. Push Context onto Current Stack
使用
sp - #offset的模式来执行,推入8个Regs
可能使用两种SPs,Main (MSP), process (PSP)
- 具体用那种看
CONTROLregister的bit 1而定 - Which is active depends on operating mode, CONTROL register bit 1(由CONTROL寄存器控制是MSP(0)还是PSP(1))
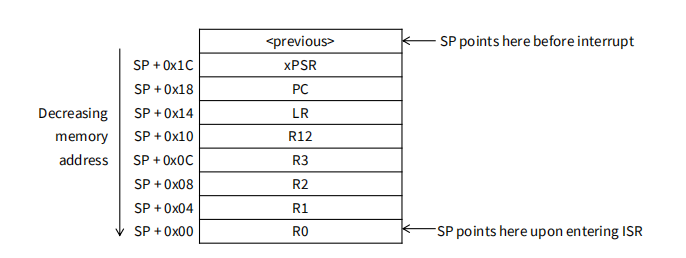
大R先存大地址
进入ISR时SP指向R0
3. Switch to Handler/Privileged Mode
Handler mode always uses MSP
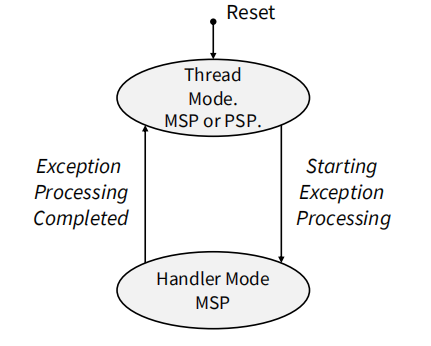
Thread 模式主要适用于用户的程序代码,Handler 模式主要适用于异常处理代码以及内核代码。可以通过 IPSR 寄存器查看处理器所处的状态。
Cortex-M 系列处理器有两种模式
- Thread Mode
- Handler Mode
Cortex 系列处理器有两种访问级别
Privileged
Unprivileged
CONTROLregister是特殊寄存器
其中第0位定义线程的特权等级: 0-Privileged Mode,1-非特权
第1位定义指针选择:0-主栈指针,1-进程指针:在处理模式时,该位始终为0
在系统 Reset之后,处理器默认是 Privileged 级别。访问级别由寄存器 control[0] 控制,当且仅当处理器运行在 Thread 模式下,该位才有效。Handler 模式只能运行在 Privileged 模式。
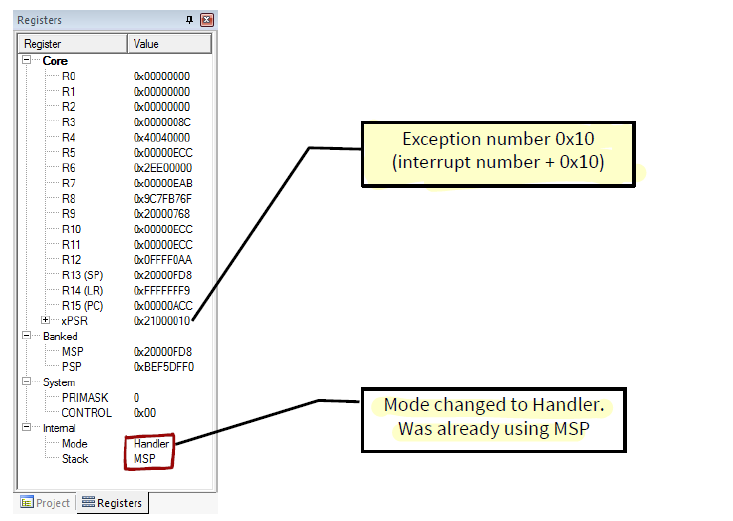
4. Load PC With Addr of Exception Handler
是根据出现的 Exception 来选特定的 Memory Address 来存入 ==PC== 中的
- 这些Memory Addr分别对应着不同的处理方式,也就是不同的 Value。
- 这个对应表存在 Vector table 中
向量地址的LSB设置为“1”表示该处理程序使用Thumb代码
IRQ中断编号,每个异常地址为四个字节,记录异常处理程序在内存中的位置
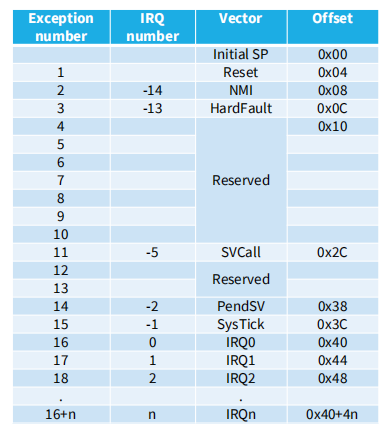
Exception num =IRQ+16
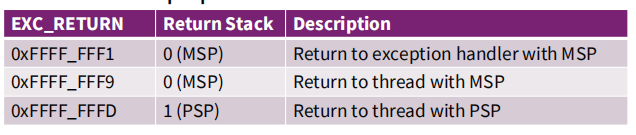
5. Load LR With EXC_RETURN Code

EXC_RETURN 码决定了要使用那种模式以及那种栈指针
restoreSP: MSP (0) or PSP (1) / return到哪个模式:Handler (0) or Thread (1)
- Handler模式还是Thread模式(Handler模式时候一定是MSP,所以三种状态)
- MSP还是PSP
EXC_RETURN value generated by CPU to provide information on how to return
6. Start Executing Exception Handler
Exception handler starts running, unless preempted(抢占) by a higher-priority exception
异常处理程序可能会在堆栈上保存额外的寄存器,例如,如果处理程序可能会调用subroutine,LR和R4必须保存
Exiting an Exception Handler
Execute instruction triggering exception return processing 执行指令触发异常返回处理
Select return stack, restore context from that stack 选择返回堆栈,从堆栈中恢复上下文
Resume execution of code at restored address 在恢复的地址恢复代码的执行
1. Return from Exception
没有“从中断返回”指令
• BX LR - Branch to address in LR by loading PC with LR contents
• POP {…, PC} - Pop address from stack into PC
使用特殊值EXC_RETURN加载到PC中以触发异常处理处理
•如果EXC_RETURN仍然在LR中,则使用BX LR
•如果EXC_RETURN已保存在堆栈中,则使用POP
2. Select Stack, Restore Context
Check EXC_RETURN (bit 2) to determine from which SP to pop the context
从堆栈中取出寄存器
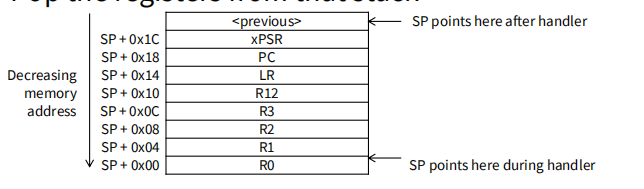
Resume Executing Previous Main Thread Code
Exception handling registers have been restored: R0, R1, R2, R3, R12, LR, PC, xPSR
SP is back to its previous value.
Back in thread mode
Timing Analysis
Interrupt Response Latency 异常响应延时
Latency = time delay
切换到中断处理程序有开销,而且浪费时间。这随着中断率的上升而增加。这会延迟我们对外部事件的响应,这对于应用程序来说可能是可接受的,也可能是不可接受的,例如对模拟波形进行采样
需要多长时间?
完成当前指令的执行或放弃该指令,将各种寄存器推到堆栈上,获取向量
Maximum Interrupt Rate
我们每秒只能处理有限数量的中断
We can only handle so many interrupts per second
- $F_{Max_Int}$ : maximum interrupt frequency
- $F_{CPU}$ : CPU clock frequency
- $C_{ISR}$ : Number of cycles ISR takes to execute
- $C_{Overhead}$: Number of cycles of overhead for saving state, vectoring, restoring state, etc.
$$
F_{Max_Int} = \frac{F_{CPU}}{C_{ISR}+C_{Overhead}}
$$
Note that model applies only when there is one interrupt in the system
==Utilization==
当处理器响应中断时,它不执行任何其他代码
- $U_{Int}$ : Utilization (fraction of processor time) consumed by interrupt processing
$$
U_{Int} = F_{Int} * \frac{C_{ISR}+C_{Overhead}}{F_{CPU}} * 100%
$$
Fint/MAX Fint
CPU looks like it’s running the other code with CPU clock speed of
$$
(1-U_{Int})*F_{CPU}
$$
以这么多的时钟频率运行其他代码
Program Design with Interrupts
如何在ISR和其他线程之间通信?
•数据缓冲
•数据完整性和竞态条件
权衡(Trade-off):ISR代码更快的响应将延迟其他代码的完成
在有多个短期限ISR的系统中,在ISR中执行关键工作,并缓冲部分结果以供后续处理
The Volatile Directive
Need to tell compiler which variables may change outside of its control
使用volatile关键字强制编译器每次使用时从内存中重新加载这些变量
volatile unsigned int num_ints;
volatile int * var; // or
int volatile * var;对变量(例如状态寄存器)的每一次C源读取都将导致一条汇编语言LDR指令